Tissue distribution, ontogeny, and hormonal regulation of xenobiotic transporters in mouse kidneys
- PMID: 19679677
- PMCID: PMC2774986
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.109.027177
Tissue distribution, ontogeny, and hormonal regulation of xenobiotic transporters in mouse kidneys
Abstract
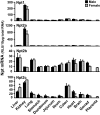
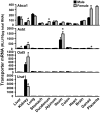
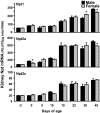
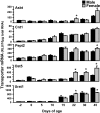
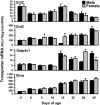
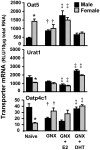
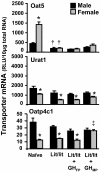
Kidneys play important roles in the elimination of numerous endogenous and exogenous chemicals. In recent years, at least 37 xenobiotic transporters have been identified in mammalian kidneys. Although much progress has been made, information on 14 of these transporters (ATP-binding cassette [Abc] a1, apical sodium bile acid transporter [Asbt], breast cancer resistance protein, concentrative nucleoside transporter 1, equilibrative nucleoside transporter [Ent] 2, Ent3, sodium-phosphate cotransporter [Npt] 1, Npt2a, Npt2b, Npt2c, organic anion transporter [Oat] 5, organic anion-transporting polypeptide [Oatp] 4c1, peptide transporter 2, and uric acid transporter [Urat] 1) in kidneys is quite limited. Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to examine the tissue distribution, ontogeny, and hormonal regulation of these 14 transporters in kidneys of mice. Other than in kidneys, Npt2b is also highly expressed in liver and lung, Npt2c in liver and colon, Asbt in ileum, and Abca1 in liver, lung, testis, ovary, and placenta of mice. Most of these (13 of 14) transporters are lowly expressed in mouse kidneys until 15 days of age, which in part contributes to the immaturity of excretory function in fetal and newborn kidneys. One exception is Ent2, which is highly expressed before birth and gradually decreases after birth until reaching adult levels at 15 days of age. Gender-divergent expression of male-predominant (Urat1 and Oatp4c1) and female-predominant (Oat5) transporters in mouse kidneys is primarily due to stimulatory effects of androgens and estrogens, respectively. In conclusion, the mRNA expression of xenobiotic transporters in kidneys is determined by tissue, age, and sex hormones.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Xenobiotic, bile acid, and cholesterol transporters: function and regulation.Pharmacol Rev. 2010 Mar;62(1):1-96. doi: 10.1124/pr.109.002014. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Pharmacol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20103563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xenobiotic and endobiotic transporter mRNA expression in the blood-testis barrier.Drug Metab Dispos. 2005 Jan;33(1):182-9. doi: 10.1124/dmd.104.001024. Epub 2004 Oct 19. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005. PMID: 15494472
-
Constitutive expression of various xenobiotic and endobiotic transporter mRNAs in the choroid plexus of rats.Drug Metab Dispos. 2003 Nov;31(11):1337-45. doi: 10.1124/dmd.31.11.1337. Drug Metab Dispos. 2003. PMID: 14570765
-
The presence of xenobiotic transporters in rat placenta.Drug Metab Dispos. 2003 Feb;31(2):153-67. doi: 10.1124/dmd.31.2.153. Drug Metab Dispos. 2003. PMID: 12527696
-
Transporter-mediated drug-drug interactions.Pharmacogenomics. 2011 Jul;12(7):1017-37. doi: 10.2217/pgs.11.44. Pharmacogenomics. 2011. PMID: 21787191 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Sequencing Quantification of Xenobiotic-Processing Genes in Various Sections of the Intestine in Comparison to the Liver of Male Mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 2016 Jun;44(6):842-56. doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.068270. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016. PMID: 27048750 Free PMC article.
-
Energy restriction does not compensate for the reduced expression of hepatic drug-processing genes in mice with aging.Drug Metab Dispos. 2010 Jul;38(7):1122-31. doi: 10.1124/dmd.110.032599. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010. PMID: 20382754 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Abnormal Water Metabolism between SD Rats and KM Mice Intoxicated by Microcystin-RR.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Feb 16;18(4):1900. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18041900. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33669356 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Gender and Various Diets on Bile Acid Profile and Related Genes in Mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 2021 Jan;49(1):62-71. doi: 10.1124/dmd.120.000166. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Drug Metab Dispos. 2021. PMID: 33093018 Free PMC article.
-
hTERT and SV40LgT Renal Cell Lines Adjust Their Transcriptional Responses After Copy Number Changes from the Parent Proximal Tubule Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 11;26(8):3607. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083607. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alnouti Y, Petrick JS, Klaassen CD. (2006) Tissue distribution and ontogeny of organic cation transporters in mice. Drug Metab Dispos 34: 477–482 - PubMed
-
- Beato M. (1989) Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell 56: 335–344 - PubMed
-
- Buist SC, Klaassen CD. (2004) Rat and mouse differences in gender-predominant expression of organic anion transporter (Oat1–3; Slc22a6–8) mRNA levels. Drug Metab Dispos 32: 620–625 - PubMed
-
- Cheng X, Klaassen CD. (2006) Regulation of mRNA expression of xenobiotic transporters by the pregnane X receptor in mouse liver, kidney, and intestine. Drug Metab Dispos 34: 1863–1867 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

