Efficient targeting of expressed and silent genes in human ESCs and iPSCs using zinc-finger nucleases
- PMID: 19680244
- PMCID: PMC4142824
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.1562
Efficient targeting of expressed and silent genes in human ESCs and iPSCs using zinc-finger nucleases
Abstract
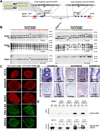
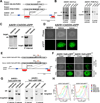
Realizing the full potential of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) requires efficient methods for genetic modification. However, techniques to generate cell type-specific lineage reporters, as well as reliable tools to disrupt, repair or overexpress genes by gene targeting, are inefficient at best and thus are not routinely used. Here we report the highly efficient targeting of three genes in human pluripotent cells using zinc-finger nuclease (ZFN)-mediated genome editing. First, using ZFNs specific for the OCT4 (POU5F1) locus, we generated OCT4-eGFP reporter cells to monitor the pluripotent state of hESCs. Second, we inserted a transgene into the AAVS1 locus to generate a robust drug-inducible overexpression system in hESCs. Finally, we targeted the PITX3 gene, demonstrating that ZFNs can be used to generate reporter cells by targeting non-expressed genes in hESCs and hiPSCs.
Figures

References
-
- Thomson JA, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Urbach A, Schuldiner M, Benvenisty N. Modeling for Lesch-Nyhan disease by gene targeting in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22:635–641. - PubMed
-
- Costa M, et al. A method for genetic modification of human embryonic stem cells using electroporation. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:792–796. - PubMed
-
- Irion S, et al. Identification and targeting of the ROSA26 locus in human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1477–1482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

