Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era
- PMID: 19680247
- PMCID: PMC2871281
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2200
Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era
Abstract
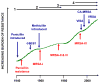
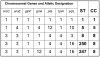
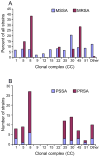
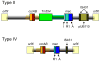
Staphylococcus aureus is notorious for its ability to become resistant to antibiotics. Infections that are caused by antibiotic-resistant strains often occur in epidemic waves that are initiated by one or a few successful clones. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) features prominently in these epidemics. Historically associated with hospitals and other health care settings, MRSA has now emerged as a widespread cause of community infections. Community or community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA) can spread rapidly among healthy individuals. Outbreaks of CA-MRSA infections have been reported worldwide, and CA-MRSA strains are now epidemic in the United States. Here, we review the molecular epidemiology of the epidemic waves of penicillin- and methicillin-resistant strains of S. aureus that have occurred since 1940, with a focus on the clinical and molecular epidemiology of CA-MRSA.
Figures
Comment in
-
Are correctional facilities amplifying the epidemic of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus?Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 Jan;8(1):83. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2200-c1. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20010953 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gorwitz RJ, et al. Changes in the prevalence of nasal colonization with Staphylococcus aureus in the United States, 2001–2004. J Infect Dis. 2008;197:1226–34. - PubMed
-
- Miller LG, Diep BA. Clinical practice: colonization, fomites, and virulence: rethinking the pathogenesis of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:752–60. - PubMed
-
- Kazakova SV, et al. A clone of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among professional football players. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:468–75. - PubMed
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:520–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

