The type III secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: infection by injection
- PMID: 19680249
- PMCID: PMC2766515
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2199
The type III secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: infection by injection
Abstract
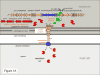
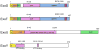
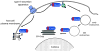
The Gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses a complex type III secretion apparatus to inject effector proteins into host cells. The configuration of this secretion machinery, the activities of the proteins that are injected by it and the consequences of this process for infection are now being elucidated. This Review summarizes our current knowledge of P. aeruginosa type III secretion, including the secretion and translocation machinery, the regulation of this machinery, and the associated chaperones and effector proteins. The features of this interesting secretion system have important implications for the pathogenesis of P. aeruginosa infections and for other type III secretion systems.
Figures


References
-
- Stryjewski ME, Sexton DJ. In: Severe infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Hauser AR, Rello J, editors. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Boston: 2003. pp. 1–15.
-
- Engel JN. In: Severe infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Hauser AR, Rello J, editors. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Boston: 2003. pp. 201–229.
-
- Yahr TL, Goranson J, Frank DW. Exoenzyme S of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is secreted by a type III secretion pathway. Mol Microbiol. 1996;22:991–1003. This is the first study to show that P. aeruginosa had a type III secretion system. - PubMed
-
- Pastor A, Chabert J, Louwagie M, Garin J, Attree I. PscF is a major component of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion needle. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2005;253:95–101. This is the first report in which the P. aeruginosa type III secretion needle complexes were visualized. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

