Bub1 and Bub3 promote the conversion from monopolar to bipolar chromosome attachment independently of shugoshin
- PMID: 19680287
- PMCID: PMC2728212
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2009.183
Bub1 and Bub3 promote the conversion from monopolar to bipolar chromosome attachment independently of shugoshin
Abstract
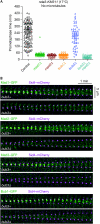
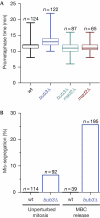
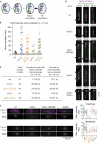
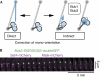
The eukaryotic spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) delays anaphase in the presence of chromosome attachment errors. Bub3 has been reported to be required for SAC activity in all eukaryotes examined so far. We find that Bub3, unlike its binding partner Bub1, is not essential for the SAC in fission yeast. As Bub3 is needed for the efficient kinetochore localization of Bub1, and of Mad1, Mad2 and Mad3, this implies that most SAC proteins do not need to be enriched at the kinetochores for the SAC to function. We find that Bub3 is also dispensable for shugoshin localization to the centromeres, which is the second known function of Bub1. Instead, Bub3, together with Bub1, has a specific function in promoting the conversion from chromosome mono-orientation to bi-orientation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Bub1-TPR Domain Interacts Directly with Mad3 to Generate Robust Spindle Checkpoint Arrest.Curr Biol. 2019 Jul 22;29(14):2407-2414.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.06.011. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31257143 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodependent recruitment of Bub1 and Bub3 to Spc7/KNL1 by Mph1 kinase maintains the spindle checkpoint.Curr Biol. 2012 May 22;22(10):891-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.051. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22521786 Free PMC article.
-
MPS1/Mph1 phosphorylates the kinetochore protein KNL1/Spc7 to recruit SAC components.Nat Cell Biol. 2012 Jun 3;14(7):746-52. doi: 10.1038/ncb2515. Nat Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22660415
-
Kinetochore-microtubule interactions "in check" by Bub1, Bub3 and BubR1: The dual task of attaching and signalling.Cell Cycle. 2008 Jun 15;7(12):1763-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.12.6180. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18594200 Review.
-
The spindle checkpoint proteins BUB1 and BUBR1: (SLiM)ming down to the basics.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Apr;47(4):352-366. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35184951 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional and Structural Characterization of Bub3·BubR1 Interactions Required for Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Signaling in Human Cells.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 20;291(21):11252-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.702142. Epub 2016 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27030009 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoregulation of Spc105 by Mps1 and PP1 regulates Bub1 localization to kinetochores.Curr Biol. 2012 May 22;22(10):900-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.052. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22521787 Free PMC article.
-
Two functionally distinct kinetochore pools of BubR1 ensure accurate chromosome segregation.Nat Commun. 2016 Jul 26;7:12256. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12256. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27457023 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM of Mitotic Checkpoint Complex-Bound APC/C Reveals Reciprocal and Conformational Regulation of Ubiquitin Ligation.Mol Cell. 2016 Aug 18;63(4):593-607. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27522463 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming inhibition in the spindle checkpoint.Genes Dev. 2009 Dec 15;23(24):2799-805. doi: 10.1101/gad.1882109. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 20008930 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

