Activating and resistance mutations of EGFR in non-small-cell lung cancer: role in clinical response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 19680293
- PMCID: PMC2849651
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.198
Activating and resistance mutations of EGFR in non-small-cell lung cancer: role in clinical response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Abstract
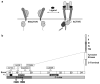
The epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR TKIs), gefitinib and erlotinib, are reversible competitive inhibitors of the tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR that bind to its adenosine-5' triphosphate-binding site. Somatic activating mutations of the EGFR gene, increased gene copy number and certain clinical and pathological features have been associated with dramatic tumor responses and favorable clinical outcomes with these agents in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The specific types of activating mutations that confer sensitivity to EGFR TKIs are present in the tyrosine kinase (TK) domain of the EGFR gene. Exon 19 deletion mutations and the single-point substitution mutation L858R in exon 21 are the most frequent in NSCLC and are termed 'classical' mutations. The NSCLC tumors insensitive to EGFR TKIs include those driven by the KRAS and MET oncogenes. Most patients who initially respond to gefitinib and erlotinib eventually become resistant and experience progressive disease. The point mutation T790M accounts for about one half of these cases of acquired resistance. Various second-generation EGFR TKIs are currently being evaluated and may have the potential to overcome T790M-mediated resistance by virtue of their irreversible inhibition of the receptor TK domain.
Figures
References
-
- Balak MN, Gong Y, Riely GJ, Somwar R, Li AR, Zakowski MF, et al. Novel D761Y and common secondary T790M mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor–mutant lung adenocarcinomas with acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6494–6501. - PubMed
-
- Bazley LA, Gullick WJ. The epidermal growth factor receptor family. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12(Suppl 1):S17–S27. - PubMed
-
- Bonomi PD, Buckingham L, Coon J. Selecting patients for treatment with epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(15 Suppl):4606s–4612s. - PubMed
-
- Cappuzzo F, Hirsch FR, Rossi E, Bartolini S, Ceresoli GL, Bemis L, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:643–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

