Temporal controls of the asymmetric cell division cycle in Caulobacter crescentus
- PMID: 19680425
- PMCID: PMC2714070
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000463
Temporal controls of the asymmetric cell division cycle in Caulobacter crescentus
Abstract
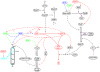
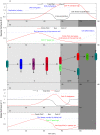
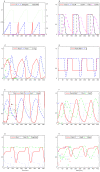
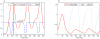
The asymmetric cell division cycle of Caulobacter crescentus is orchestrated by an elaborate gene-protein regulatory network, centered on three major control proteins, DnaA, GcrA and CtrA. The regulatory network is cast into a quantitative computational model to investigate in a systematic fashion how these three proteins control the relevant genetic, biochemical and physiological properties of proliferating bacteria. Different controls for both swarmer and stalked cell cycles are represented in the mathematical scheme. The model is validated against observed phenotypes of wild-type cells and relevant mutants, and it predicts the phenotypes of novel mutants and of known mutants under novel experimental conditions. Because the cell cycle control proteins of Caulobacter are conserved across many species of alpha-proteobacteria, the model we are proposing here may be applicable to other genera of importance to agriculture and medicine (e.g., Rhizobium, Brucella).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Novak B, Pataki Z, Ciliberto A, Tyson JJ. Mathematical model of the cell division cycle of fission yeast. Chaos. 2001;11:277–286. - PubMed
-
- Novak B, Csikasz-Nagy A, Gyorffy B, Chen K, Tyson JJ. Mathematical model of the fission yeast cell cycle with checkpoint controls at the G1/S, G2/M and metaphase/anaphase transitions. BiophysChem. 1998;72:185–200. - PubMed
-
- Tyson JJ, Chen K, Novak B. Network dynamics and cell physiology. NatRevMolCell Biol. 2001;2:908–916. - PubMed
-
- Marlovits G, Tyson CJ, Novak B, Tyson JJ. Modeling M-phase control in Xenopus oocyte extracts: the surveillance mechanism for unreplicated DNA. BiophysChem. 1998;72:169–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

