Overload-induced skeletal muscle extracellular matrix remodelling and myofibre growth in mice lacking IL-6
- PMID: 19681796
- PMCID: PMC3044433
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2009.02029.x
Overload-induced skeletal muscle extracellular matrix remodelling and myofibre growth in mice lacking IL-6
Abstract
Aim: Overloading healthy skeletal muscle produces myofibre hypertrophy and extracellular matrix remodelling, and these processes are thought to be interdependent for producing muscle growth. Inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene expression is induced in overloaded skeletal muscle, and the loss of this IL-6 induction can attenuate the hypertrophic response to overload (OV). Although the OV induction of IL-6 in skeletal muscle may be an important regulator of inflammatory processes and satellite cell proliferation, less is known about its role in the regulation of extracellular matrix remodelling. The purpose of the current study was to examine if OV-induced extracellular matrix remodelling, muscle growth, and associated gene expression were altered in mice that lack IL-6, when compared with wild-type mice.
Methods: Male C57/BL6 (WT) and C57/BL6 x IL-6(-/-) (IL-6(-/-)) mice (10 weeks of age) were assigned to either a sham control or synergist ablation OV treatments for 3, 21 or 56 days.
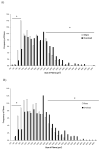
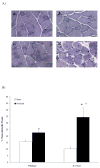
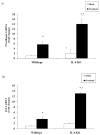
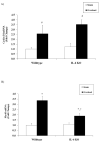
Result: Plantaris muscle mass increased 59% in WT and 116% in IL-6(-/-) mice after 21 day OV. Myofibre CSA was also increased by 21 day OV in both WT and IL-6(-/-) mice. OV induced a twofold greater increase in the volume of non-contractile tissue in IL-6(-/-) muscle compared to WT. OV also induced a significantly greater accumulation of hydroxyproline and procollagen-1 mRNA in IL-6(-/-) muscle, when compared with WT muscle after 21 day OV. Transforming growth factor-beta and insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA expression were also induced to a greater extent in IL-6(-/-) muscle when compared with WT muscle after 21 day OV. There was no effect of IL-6 loss on the induction of myogenin, and cyclin D1 mRNA expression after 3 day OV. However, MyoD mRNA expression in 3 day OV IL-6(-/-) muscle was attenuated when compared with WT OV mice.
Conclusion: IL-6 appears to be necessary for the normal regulation of extracellular matrix remodelling during OV-induced growth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Adams GR, Haddad F, Baldwin KM. Time course of changes in markers of myogenesis in overloaded rat skeletal muscles. J Appl Physiol. 1999;87:1705–1712. - PubMed
-
- Baltgalvis KA, Berger FG, Pena MM, Davis JM, Muga SJ, Carson JA. Interleukin-6 and cachexia in ApcMin/+ mice. American journal of physiology. 2008;294:R393–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

