Penelope's web: using alpha-latrotoxin to untangle the mysteries of exocytosis
- PMID: 19682210
- PMCID: PMC3145131
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06329.x
Penelope's web: using alpha-latrotoxin to untangle the mysteries of exocytosis
Abstract
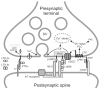
For more than three decades, the venom of the black widow spider and its principal active components, latrotoxins, have been used to induce release of neurotransmitters and hormones and to study the mechanisms of exocytosis. Given the complex nature of alpha--latrotoxin (alpha-LTX) actions, this research has been continuously overshadowed by many enigmas, misconceptions and perpetual changes of the underlying hypotheses. Some of the toxin's mechanisms of action are still not completely understood. Despite all these difficulties, the extensive work of several generations of neurobiologists has brought about a great deal of fascinating insights into pre-synaptic processes and has led to the discovery of several novel proteins and synaptic systems. For example, alpha-LTX studies have contributed to the widespread acceptance of the vesicular theory of transmitter release. Pre-synaptic receptors for alpha-LTX--neurexins, latrophilins and protein tyrosine phosphatase sigma--and their endogenous ligands have now become centrepieces of their own areas of research, with a potential of uncovering new mechanisms of synapse formation and regulation that may have medical implications. However, any future success of alpha-LTX research will require a better understanding of this unusual natural tool and a more precise dissection of its multiple mechanisms.
Figures


References
-
- Adam-Vizi V, Deri Z, Bors P, Tretter L. Lack of involvement of [Ca2+]i in the external Ca2+-independent release of acetylcholine evoked by veratridine, ouabain and α-latrotoxin: possible role of [Na+]i. J. Physiol. Paris. 1993;87:43–50. - PubMed
-
- Aguado F, Gombau L, Majo G, Marsal J, Blanco J, Blasi J. Regulated secretion is impaired in AtT-20 endocrine cells stably transfected with botulinum neurotoxin type A light chain. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:26005–26008. - PubMed
-
- Angaut-Petit D, Molgo J, Faille L, Juzans P, Takahashi M. Incorporation of synaptotagmin II to the axolemma of botulinum type-A poisoned mouse motor endings during enhanced quantal acetylcholine release. Brain Res. 1998;797:357–360. - PubMed
-
- Ashton AC, et al. Tetramerisation of α-latrotoxin by divalent cations is responsible for toxin-induced non-vesicular release and contributes to the Ca2+-dependent vesicular exocytosis from synaptosomes. Biochimie. 2000;82:453–468. - PubMed
-
- Ashton AC, Ushkaryov YA. Properties of synaptic vesicle pools in mature central nerve terminals. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:37278–37288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

