SirA enforces diploidy by inhibiting the replication initiator DnaA during spore formation in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 19682252
- PMCID: PMC2992877
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06825.x
SirA enforces diploidy by inhibiting the replication initiator DnaA during spore formation in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
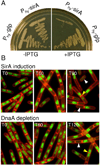
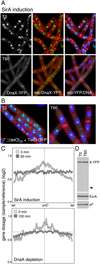
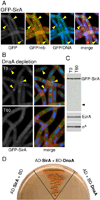
How cells maintain their ploidy is relevant to cellular development and disease. Here, we investigate the mechanism by which the bacterium Bacillus subtilis enforces diploidy as it differentiates into a dormant spore. We demonstrate that a sporulation-induced protein SirA (originally annotated YneE) blocks new rounds of replication by targeting the highly conserved replication initiation factor DnaA. We show that SirA interacts with DnaA and displaces it from the replication origin. As a result, expression of SirA during growth rapidly blocks replication and causes cell death in a DnaA-dependent manner. Finally, cells lacking SirA over-replicate during sporulation. These results support a model in which induction of SirA enforces diploidy by inhibiting replication initiation as B. subtilis cells develop into spores.
Figures




References
-
- Bastedo DP, Marczynski GT. CtrA response regulator binding to the Caulobacter chromosome replication origin is required during nutrient and antibiotic stress as well as during cell cycle progression. Mol Microbiol. 2009;72:139–154. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Yehuda S, Losick R. Asymmetric cell division in B. subtilis involves a spiral-like intermediate of the cytokinetic protein FtsZ. Cell. 2002;109:257–266. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Yehuda S, Rudner DZ, Losick R. RacA, a bacterial protein that anchors chromosomes to the cell poles. Science. 2003;299:532–536. - PubMed
-
- Berkmen MB, Grossman AD. Subcellular positioning of the origin region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome is independent of sequences within oriC, the site of replication initiation, and the replication initiator DnaA. Mol Microbiol. 2007;63:150–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

