Intrinsic neuronal plasticity in the juxtacapsular nucleus of the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis (jcBNST)
- PMID: 19683025
- PMCID: PMC2935256
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.08.003
Intrinsic neuronal plasticity in the juxtacapsular nucleus of the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis (jcBNST)
Abstract
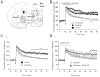
The juxtacapsular nucleus of the anterior division of the BNST (jcBNST) receives robust glutamatergic projections from the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala (BLA), the postpiriform transition area, and the insular cortex as well as dopamine (DA) inputs from the midbrain. In turn the jcBNST sends GABAergic projections to the medial division of the central nucleus of the amygdala (CEAm) as well as other brain regions. We recently described a form of long-term potentiation of the intrinsic excitability (LTP-IE) of neurons of the juxtacapsular nucleus of BNST (jcBNST) in response to high-frequency stimulation (HFS) of the stria terminalis that was impaired during protracted withdrawal from alcohol, cocaine, and heroin and in rats chronically treated with corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) intracerebroventricularly. Here we show that DAergic neurotransmission is required for the induction of LTP-IE of jcBNST neurons through dopamine (DA) D1 receptors. Thus, activation of the central CRF stress system and altered DAergic neurotransmission during protracted withdrawal from alcohol and drugs of abuse may contribute to the disruption of LTP-IE in the jcBNST. Impairment of this form of intrinsic neuronal plasticity in the jcBNST could result in inadequate neuronal integration and reduced inhibition of the CEA, contributing to the negative affective state that characterizes protracted abstinence in post-dependent individuals. These results provide a novel neurobiological target for vulnerability to alcohol and drug dependence.
Figures
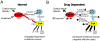
References
-
- Adamec R. The relationship between the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the cat: an evoked potential and single cell study. Behav Neural Biol. 1989;52:295–320. - PubMed
-
- Adriani W, Felici A, Sargolini F, Roullet P, Usiello A, Oliverio A, Mele A. Nmethyl- D-aspartate and dopamine receptor involvement in the modulation of locomotor activity and memory processes. Exp Brain Res. 1998;123:52–59. - PubMed
-
- Aizenman C, Linden D. Rapid, synaptically driven increases in the intrinsic excitability of cerebellar deep nuclear neuronsV. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:109–111. - PubMed
-
- Alheid G, de Olmos J, CA B. Amygdala and extended amygdala. In: Paxinos G, editor. The Rat Nervous System. 2nd. San Diego: Academic Press; 1995. pp. 495–578.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AA006420/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AA015080/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA004043/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA008459/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA016587/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA016587/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA013191/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA006420/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA004398/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013191/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA013821/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA017371/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013821/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA006420/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA008459/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA004398/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA008459/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA004043/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

