Potential of immunomodulatory host defense peptides as novel anti-infectives
- PMID: 19683819
- PMCID: PMC7114281
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.07.004
Potential of immunomodulatory host defense peptides as novel anti-infectives
Abstract
A fundamentally new strategy for the treatment of infectious disease is the modulation of host immune responses to enhance clearance of infectious agents and reduce tissue damage due to inflammation. Antimicrobial host defense peptides have been investigated for their potential as a new class of antimicrobial drugs. Recently their immunomodulatory activities have begun to be appreciated. Modulation of innate immunity by synthetic variants of host defense peptides, called innate defense regulators (IDRs), is protective without direct antimicrobial action. We discuss the potential and current limitations in exploiting the immunomodulatory activity of IDRs as a novel anti-infective pathway. IDRs show significant promise and current research is uncovering mechanistic information that will aid in the future development of IDRs for clinical use.
Figures
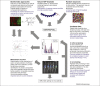
References
-
- WHO (2008) World Health Statistics 2008, World Health Organisation Press
-
- Spellberg B. The epidemic of antibiotic resistant infections: a call to action for the medical community from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008;46:155–164. - PubMed
-
- Waldmann T.A. Immunotherapy: past, present and future. Nat. Med. 2003;9:269–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

