Capsular polysaccharide production in Enterococcus faecalis and contribution of CpsF to capsule serospecificity
- PMID: 19684130
- PMCID: PMC2753019
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00592-09
Capsular polysaccharide production in Enterococcus faecalis and contribution of CpsF to capsule serospecificity
Abstract
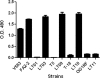
Many bacterial species produce capsular polysaccharides that contribute to pathogenesis through evasion of the host innate immune system. The gram-positive pathogen Enterococcus faecalis was previously reported to produce one of four capsule serotypes (A, B, C, or D). Previous studies describing the four capsule serotypes of E. faecalis were based on immunodetection methods; however, the underlying genetics of capsule production did not fully support these findings. Previously, it was shown that capsule production for serotype C (Maekawa type 2) was dependent on the presence of nine open reading frames (cpsC to cpsK). Using a novel genetic system, we demonstrated that seven of the nine genes in the cps operon are essential for capsule production, indicating that serotypes A and B do not make a capsular polysaccharide. In support of this observation, we showed that serotype C and D capsule polysaccharides mask lipoteichoic acid from detection by agglutinating antibodies. Furthermore, we determined that the genetic basis for the difference in antigenicity between serotypes C and D is the presence of cpsF in serotype C strains. High-pH anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection analysis of serotype C and D capsules indicated that cpsF is responsible for glucosylation of serotype C capsular polysaccharide in E. faecalis.
Figures




References
-
- Behnke, D., M. S. Gilmore, and J. J. Ferretti. 1981. Plasmid pGB301, a new multiple resistance streptococcal cloning vehicle and its use in cloning of a gentamicin/kanamycin resistance determinant. Mol. Gen. Genet. 182:414-421. - PubMed
-
- Bottone, E. J. 1999. Encapsulated Enterococcus faecalis: role of encapsulation in persistence in mouse peritoneum in absence of mouse lethality. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 33:65-68. - PubMed
-
- Bruserud, O., O. Wendelbo, and K. Paulsen. 2004. Lipoteichoic acid derived from Enterococcus faecalis modulates the functional characteristics of both normal peripheral blood leukocytes and native human acute myelogenous leukemia blasts. Eur. J. Haematol. 73:340-350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

