Investigation of associations of Yarrowia lipolytica, Staphylococcus xylosus, and Lactococcus lactis in culture as a first step in microbial interaction analysis
- PMID: 19684166
- PMCID: PMC2765154
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00228-09
Investigation of associations of Yarrowia lipolytica, Staphylococcus xylosus, and Lactococcus lactis in culture as a first step in microbial interaction analysis
Abstract
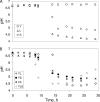
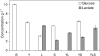
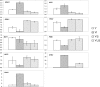
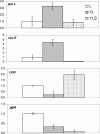
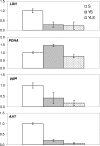
The interactions that may occur between microorganisms in different ecosystems have not been adequately studied yet. We investigated yeast-bacterium interactions in a synthetic medium using different culture associations involving the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica 1E07 and two bacteria, Staphylococcus xylosus C2a and Lactococcus lactis LD61. The growth and biochemical characteristics of each microorganism in the different culture associations were studied. The expression of genes related to glucose, lactate, and amino acid catabolism was analyzed by reverse transcription followed by quantitative PCR. Our results show that the growth of Y. lipolytica 1E07 is dramatically reduced by the presence of S. xylosus C2a. As a result of a low amino acid concentration in the medium, the expression of Y. lipolytica genes involved in amino acid catabolism was downregulated in the presence of S. xylosus C2a, even when L. lactis was present in the culture. Furthermore, the production of lactate by both bacteria had an impact on the lactate dehydrogenase gene expression of the yeast, which increased up to 30-fold in the three-species culture compared to the Y. lipolytica 1E07 pure culture. S. xylosus C2a growth dramatically decreased in the presence of Y. lipolytica 1E07. The growth of lactic acid bacteria was not affected by the presence of S. xylosus C2a or Y. lipolytica 1E07, although the study of gene expression showed significant variations.
Figures

References
-
- Addis, E., G. H. Fleet, J. M. Cox, D. Kolak, and T. Leung. 2001. The growth, properties and interactions of yeasts and bacteria associated with the maturation of Camembert and blue-veined cheeses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 69:25-36. - PubMed
-
- Álvarez-Martín, P., A. B. Flórez, A. Hernández-Barranco, and B. Mayo. 2008. Interaction between dairy yeasts and lactic acid bacteria strains during milk fermentation. Food Control 19:62-70.
-
- Barnett, J. A., R. W. Payne, and D. Yarrow. 2000. Yeasts: characteristics and identification. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

