Modulation of reactive oxygen species by Rac1 or catalase prevents asbestos-induced pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 19684199
- PMCID: PMC2777495
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.90590.2008
Modulation of reactive oxygen species by Rac1 or catalase prevents asbestos-induced pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
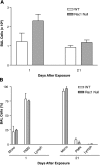
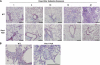
The release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cytokines by alveolar macrophages has been demonstrated in asbestos-induced pulmonary fibrosis, but the mechanism linking alveolar macrophages to the pathogenesis is not known. The GTPase Rac1 is a second messenger that plays an important role in host defense. In this study, we demonstrate that Rac1 null mice are protected from asbestos-induced pulmonary fibrosis, as determined by histological and biochemical analysis. We hypothesized that Rac1 induced pulmonary fibrosis via generation of ROS. Asbestos increased TNF-alpha and ROS in a Rac1-dependent manner. TNF-alpha was elevated only 1 day after exposure, whereas ROS generation progressively increased in bronchoalveolar lavage cells obtained from wild-type (WT) mice. To determine whether ROS generation contributed to pulmonary fibrosis, we overexpressed catalase in WT monocytes and observed a decrease in ROS generation in vitro. More importantly, administration of catalase to WT mice attenuated the development of fibrosis in vivo. For the first time, these results demonstrate that Rac1 plays a crucial role in asbestos-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Moreover, it suggests that a simple intervention may be useful to prevent progression of the disease.
Figures





References
-
- Adam O, Frost G, Custodis F, Sussman MA, Schafers HJ, Bohm M, Laufs U. Role of Rac1 GTPase activation in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol 50: 359–367, 2007 - PubMed
-
- . Diagnosis and initial management of nonmalignant diseases related to asbestos. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170: 691–715, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Begin R, Martel M, Desmarais Y, Drapeau G, Boileau R, Rola-Pleszczynski M, Masse S. Fibronectin and procollagen 3 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage of asbestos-exposed human subjects and sheep. Chest 89: 237–243, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Bokoch GM. Regulation of innate immunity by Rho GTPases. Trends Cell Biol 15: 163–171, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Brenner DA, O'Hara M, Angel P, Chojkier M, Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-α. Nature 337: 661–663, 1989 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

