A serine carboxypeptidase-like acyltransferase is required for synthesis of antimicrobial compounds and disease resistance in oats
- PMID: 19684243
- PMCID: PMC2751944
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.065870
A serine carboxypeptidase-like acyltransferase is required for synthesis of antimicrobial compounds and disease resistance in oats
Abstract
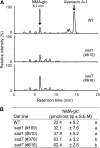
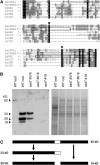
Serine carboxypeptidase-like (SCPL) proteins have recently emerged as a new group of plant acyltransferases. These enzymes share homology with peptidases but lack protease activity and instead are able to acylate natural products. Several SCPL acyltransferases have been characterized to date from dicots, including an enzyme required for the synthesis of glucose polyesters that may contribute to insect resistance in wild tomato (Solanum pennellii) and enzymes required for the synthesis of sinapate esters associated with UV protection in Arabidopsis thaliana. In our earlier genetic analysis, we identified the Saponin-deficient 7 (Sad7) locus as being required for the synthesis of antimicrobial triterpene glycosides (avenacins) and for broad-spectrum disease resistance in diploid oat (Avena strigosa). Here, we report on the cloning of Sad7 and show that this gene encodes a functional SCPL acyltransferase, SCPL1, that is able to catalyze the synthesis of both N-methyl anthraniloyl- and benzoyl-derivatized forms of avenacin. Sad7 forms part of an operon-like gene cluster for avenacin synthesis. Oat SCPL1 (SAD7) is the founder member of a subfamily of monocot-specific SCPL proteins that includes predicted proteins from rice (Oryza sativa) and other grasses with potential roles in secondary metabolism and plant defense.
Figures
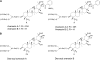




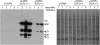
Comment in
-
Evolution of serine carboxypeptidase-like acyltransferases in the monocots.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Feb;5(2):193-5. doi: 10.4161/psb.5.2.11093. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20173416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumert, A., Milkowski, C., Schmidt, J., Nimtz, M., Wray, V., and Strack, D. (2005). Formation of a complex pattern of sinapate esters in Brassica napus seeds, catalysed by enzymes of a serine carboxypeptidase-like acyltransferase family. Phytochemistry. 66: 1334–1345. - PubMed
-
- Cañizares, M.C., Liu, L., Perrin, Y., Tsakiris, E., and Lomonossoff, G.P. (2006). A bipartite system for the constitutive and inducible expression of high levels of foreign proteins in plants. Plant Biotechnol. 4: 183–193. - PubMed
-
- D'Auria, J.C. (2006). Acyltransferases in plants: A good time to be BAHD. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 9: 331–340. - PubMed
-
- Dixon, R.A. (2001). Natural products and plant disease resistance. Nature 441: 843–847. - PubMed
-
- Dudareva, N., D'Auria, J.C., Nam, K.H., Raguso, R.A., and Pichersky, E. (1998). Acetyl-CoA:benzylalcohol acetyltransferase - An enzyme involved in floral scent production in Clarkia breweri. Plant J. 14: 297–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/J/00000166/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/J/00000614/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E008984/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E009913/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E009912/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

