Enterorhabdus caecimuris sp. nov., a member of the family Coriobacteriaceae isolated from a mouse model of spontaneous colitis, and emended description of the genus Enterorhabdus Clavel et al. 2009
- PMID: 19684311
- PMCID: PMC3052451
- DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.015016-0
Enterorhabdus caecimuris sp. nov., a member of the family Coriobacteriaceae isolated from a mouse model of spontaneous colitis, and emended description of the genus Enterorhabdus Clavel et al. 2009
Abstract
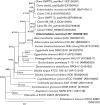
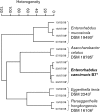
The C3H/HeJBir mouse model of intestinal inflammation was used for isolation of a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacterium (B7(T)) from caecal suspensions. On the basis of partial 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, strain B7(T) was a member of the class Actinobacteria, family Coriobacteriaceae, and was related closely to Enterorhabdus mucosicola Mt1B8(T) (97.6 %). The major fatty acid of strain B7(T) was C(16 : 0) (19.1 %) and the respiratory quinones were mono- and dimethylated. Cells were aerotolerant, but grew only under anoxic conditions. Strain B7(T) did not convert the isoflavone daidzein and was resistant to cefotaxime. The results of DNA-DNA hybridization experiments and additional physiological and biochemical tests allowed the genotypic and phenotypic differentiation of strain B7(T) from the type strain of E. mucosicola. Therefore, strain B7(T) represents a novel species, for which the name Enterorhabdus caecimuris sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is B7(T) (=DSM 21839(T) =CCUG 56815(T)).
Figures
References
-
- Cashion, P., Holder-Franklin, M. A., McCully, J. & Franklin, M. (1977). A rapid method for the base ratio determination of bacterial DNA. Anal Biochem 81, 461–466. - PubMed
-
- Clavel, T., Charrier, C., Braune, A., Wenning, M., Blaut, M. & Haller, D. (2009). Isolation of bacteria from the ileal mucosa of TNFdeltaARE mice and description of Enterorhabdus mucosicola gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59, 1805–1812. - PubMed
-
- De Ley, J., Cattoir, H. & Reynaerts, A. (1970). The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12, 133–142. - PubMed
-
- Duck, L. W., Walter, M. R., Novak, J., Kelly, D., Tomasi, M., Cong, Y. & Elson, C. O. (2007). Isolation of flagellated bacteria implicated in Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13, 1191–1201. - PubMed
-
- Hall, T. A. (1999). BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41, 95–98.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

