Ultradian hormone stimulation induces glucocorticoid receptor-mediated pulses of gene transcription
- PMID: 19684579
- PMCID: PMC6711162
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1922
Ultradian hormone stimulation induces glucocorticoid receptor-mediated pulses of gene transcription
Abstract
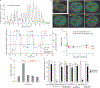
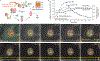
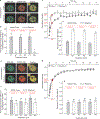
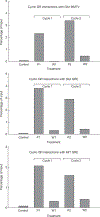
Studies on glucocorticoid receptor (GR) action typically assess gene responses by long-term stimulation with synthetic hormones. As corticosteroids are released from adrenal glands in a circadian and high-frequency (ultradian) mode, such treatments may not provide an accurate assessment of physiological hormone action. Here we demonstrate that ultradian hormone stimulation induces cyclic GR-mediated transcriptional regulation, or gene pulsing, both in cultured cells and in animal models. Equilibrium receptor-occupancy of regulatory elements precisely tracks the ligand pulses. Nascent RNA transcripts from GR-regulated genes are released in distinct quanta, demonstrating a profound difference between the transcriptional programs induced by ultradian and constant stimulation. Gene pulsing is driven by rapid GR exchange with response elements and by GR recycling through the chaperone machinery, which promotes GR activation and reactivation in response to the ultradian hormone release, thus coupling promoter activity to the naturally occurring fluctuations in hormone levels. The GR signalling pathway has been optimized for a prompt and timely response to fluctuations in hormone levels, indicating that biologically accurate regulation of gene targets by GR requires an ultradian mode of hormone stimulation.
Figures
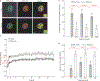
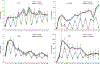
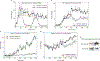

Comment in
-
Steroid hormone pulsing drives cyclic gene expression.Nat Cell Biol. 2009 Sep;11(9):1051-3. doi: 10.1038/ncb0909-1051. Nat Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19724259
References
-
- Lightman SL et al. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function. Arch. Physiol Biochem. 110, 90–93 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Lightman SL Patterns of exposure to glucocorticoid receptor ligand. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 34, 1117–1118 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Droste SK et al. Corticosterone levels in the brain show a distinct ultradian rhythm but a delayed response to forced swim stress. Endocrinology 149, 3244–3253 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Young EA, Abelson J & Lightman SL Cortisol pulsatility and its role in stress regulation and health. Front Neuroendocrinol. 25, 69–76 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Lewis JG, Bagley CJ, Elder PA, Bachmann AW & Torpy DJ Plasma free cortisol fraction reflects levels of functioning corticosteroid-binding globulin. Clin. Chim. Acta 359, 189–194 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

