Mutation of SHOC2 promotes aberrant protein N-myristoylation and causes Noonan-like syndrome with loose anagen hair
- PMID: 19684605
- PMCID: PMC2765465
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.425
Mutation of SHOC2 promotes aberrant protein N-myristoylation and causes Noonan-like syndrome with loose anagen hair
Abstract
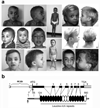
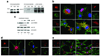
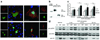
N-myristoylation is a common form of co-translational protein fatty acylation resulting from the attachment of myristate to a required N-terminal glycine residue. We show that aberrantly acquired N-myristoylation of SHOC2, a leucine-rich repeat-containing protein that positively modulates RAS-MAPK signal flow, underlies a clinically distinctive condition of the neuro-cardio-facial-cutaneous disorders family. Twenty-five subjects with a relatively consistent phenotype previously termed Noonan-like syndrome with loose anagen hair (MIM607721) shared the 4A>G missense change in SHOC2 (producing an S2G amino acid substitution) that introduces an N-myristoylation site, resulting in aberrant targeting of SHOC2 to the plasma membrane and impaired translocation to the nucleus upon growth factor stimulation. Expression of SHOC2(S2G) in vitro enhanced MAPK activation in a cell type-specific fashion. Induction of SHOC2(S2G) in Caenorhabditis elegans engendered protruding vulva, a neomorphic phenotype previously associated with aberrant signaling. These results document the first example of an acquired N-terminal lipid modification of a protein causing human disease.
Figures

References
-
- Resh MD. Trafficking and signaling by fatty-acylated and prenylated proteins. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:584–590. - PubMed
-
- Farazi TA, Waksman G, Gordon JI. The biology and enzymology of protein N-myristoylation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:39501–39504. - PubMed
-
- Sieburth DS, Sun Q, Han M. SUR-8, a conserved Ras-binding protein with leucine-rich repeats, positively regulates Ras-mediated signaling in C. elegans. Cell. 1998;94:119–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

