Polygalasaponin XXXII from Polygala tenuifolia root improves hippocampal-dependent learning and memory
- PMID: 19684611
- PMCID: PMC4007183
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.112
Polygalasaponin XXXII from Polygala tenuifolia root improves hippocampal-dependent learning and memory
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to investigate the cognition-enhancing activity and underlying mechanisms of a triterpenoid saponin (polygalasaponin XXXII, PGS32) isolated from the roots of Polygala tenuifolia Willd.
Methods: The Morris water maze was used to evaluate the spatial learning and memory of mice. To detect the basic properties of synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation (LTP) in the dentate gyrus of rats, electrophysiological recordings were made of evoked potentials. Western blotting analysis and immunofluorescence assays were used to determine the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB), synapsin I and the expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
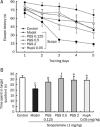
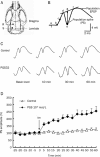
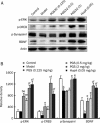
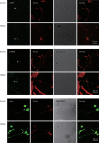
Results: When administered at 0.125, 0.5, or 2 mg/kg, PGS32 could significantly prevent scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments in mice. Intracerebroventricular (icv) administration of PGS32 greatly enhanced basic synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus of rats and induced LTP. In primary hippocampal neurons, as well as in the hippocampus of maze-trained mice, PGS32 activated the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade by promoting phosphorylation of ERK, CREB and synapsin I. The expression of BDNF was also greatly enhanced in the hippocampus.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that PGS32 can improve hippocampus-dependent learning and memory, possibly through improvement of synaptic transmission, activation of the MAP kinase cascade and enhancement of the level of BDNF. Therefore, PGS32 shows promise as a potential cognition-enhancing therapeutic drug.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polygalasaponin XXXII, a triterpenoid saponin from Polygalae Radix, attenuates scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments in mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016 Aug;37(8):1045-53. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.17. Epub 2016 May 16. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016. PMID: 27180981 Free PMC article.
-
Polygalasaponin F induces long-term potentiation in adult rat hippocampus via NMDA receptor activation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Apr;33(4):431-7. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.199. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22286914 Free PMC article.
-
Danggui-Jakyak-San enhances hippocampal long-term potentiation through the ERK/CREB/BDNF cascade.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 4;175:481-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.012. Epub 2015 Oct 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26453932
-
Polygala tenuifolia: a source for anti-Alzheimer's disease drugs.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):410-416. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1758732. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 32429787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saponin components in Polygala tenuifolia as potential candidate drugs for treating dementia.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1431894. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1431894. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39050746 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine in Neuroprotection after Brain Insults with Special Reference to Radioprotection.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Nov 26;2018:2767208. doi: 10.1155/2018/2767208. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30598683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Alzheimer's Disease: A Focus on Natural Products and Phytomedicines.CNS Drugs. 2019 May;33(5):457-480. doi: 10.1007/s40263-019-00619-1. CNS Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30900203 Review.
-
Polygalae Radix Attenuates Methamphetamine-Induced Behavioral Sensitization Through the TrkB/ERK Pathway in the Caudate Putamen of Mice.Neurochem Res. 2025 Mar 17;50(2):120. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04368-0. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40095175
-
New Potential Pharmacological Functions of Chinese Herbal Medicines via Regulation of Autophagy.Molecules. 2016 Mar 17;21(3):359. doi: 10.3390/molecules21030359. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26999089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced Consolidation, Reinstatement, and Renewal of Conditioned Fear Memory by Repetitive Treatment of Radix Polygalae in Mice.Front Psychiatry. 2017 May 31;8:97. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00097. eCollection 2017. Front Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28620325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakata Y, Chida R, Ishige K, Edagawa Y, Tadano T, Ito Y. Effect of a nutritive-tonic drink on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005;28:1886–91. - PubMed
-
- Sun XL, Ito H, Masuoka T, Kamei C, Hatano T. Effect of Polygala tenuifolia root extract on scopolamine-induced impairment of rat spatial cognition in an eight-arm radial maze task. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30:1727–31. - PubMed
-
- Park CH, Choi SH, Koo JW, Seo JH, Kim HS, Jeong SJ, et al. Novel cognitive improving and neuroprotective activities of Polygala tenuifolia Willdenow extract, BT-11. J Neurosci Res. 2002;70:484–92. - PubMed
-
- Ikeya Y, Takeda S, Tunakawa M, Karakida H, Toda K, Yamaguchi T, et al. Cognitive improving and cerebral protective effects of acylated oligosaccharides in Polygala tenuifolia. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27:1081–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

