Genetic and environmental factors influencing human diseases with telomere dysfunction
- PMID: 19684885
- PMCID: PMC2719702
Genetic and environmental factors influencing human diseases with telomere dysfunction
Abstract
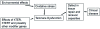
Both genetic and environmental factors have been implicated in the mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of serious and fatal forms of human blood disorder (acquired aplastic anemia, AA) and lung disease (idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, IPF). We and other researchers have recently shown that naturally occurring mutations in genes encoding the telomere maintenance complex (telomerase) may predispose patients to the development of AA or IPF. Epidemiological data have shown that environmental factors can also cause and/or exacerbate the pathogenesis of these diseases. The exact mechanisms that these germ-line mutations in telomere maintenance genes coupled with environmental insults lead to ineffective hematopoiesis in AA and lung scarring in IPF are not well understood, however. In this article, we provide a summary of evidence for environmental and genetic factors influencing the diseases. These studies provide important insights into the interplay between environmental and genetic factors leading to human diseases with telomere dysfunction.
Keywords: Telomeres; aplastic anemia; dyskeratosis congenita; environmental factors; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; telomerase.
Figures


References
-
- Blackburn EH. Switching and signaling at the telomere. Cell. 2001;106:661–673. - PubMed
-
- Griffith JD, Comeau L, Rosenfield S, Stansel RM, Bianchi A, Moss H, de Lange T. Mammalian telomeres end in a large duplex loop. Cell. 1999;97:503–514. - PubMed
-
- Olovnikov AM. A theory of marginotomy. The incomplete copying of template margin in enzymic synthesis of polynucleotides and biological significance of the phenomenon. J Theor Biol. 1973;41:181–190. - PubMed
-
- Watson JD. Origin of concatemeric T7 DNA. Nat New Biol. 1972;239:197–201. - PubMed
-
- Harley CB, Futcher AB, Greider CW. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990;345:458–460. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
