Attention moderates the processing of inhibitory information in primary psychopathy
- PMID: 19685952
- PMCID: PMC2729538
- DOI: 10.1037/a0016480
Attention moderates the processing of inhibitory information in primary psychopathy
Abstract
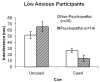
Primary psychopathic individuals are less apt to reevaluate or change their behavior in response to stimuli outside of their current focus of attention. According to the response modulation hypothesis, this tendency reflects a lack of responsivity to important peripheral information and undermines adaptive self-regulation. To evaluate this hypothesis, the authors administered a response competition (flanker-type) task and manipulated focus of visual attention. They predicted that psychopathic individuals would display significantly less interference to response incongruent information than nonpsychopathic participants when attention was cued to the target location but display normal interference when there was no prepotent focus of attention. The results confirmed this hypothesis and are consistent with the contention that attention moderates psychopathic individuals' responsivity to inhibitory cues. Implications of this attentional anomaly for psychopathic traits and behavior are discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Arnett PA, Smith SS, Newman JP. Approach and avoidance motivation in psychopathic criminal offenders during passive avoidance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1997;72:1413–1428. - PubMed
-
- Blair RJR. The roles of orbital frontal cortex in the modulation of antisocial behavior. Brain and Cognition. 2004;55:198–208. - PubMed
-
- Blair RJR, Mitchell DGV, Richell RA, Kelly S, Leonard A, Newman C, Scott SK. Turning a deaf ear to fear: Impaired recognition of vocal affect in psychopathic individuals. Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 2002;111:682–686. - PubMed
-
- Botvinick M, Nystrom LE, Fissell K, Carter CS, Cohen JD. Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature. 1999;402:179–181. - PubMed
-
- Brinkley CA, Newman JP, Widiger T, Lynam D. Two approaches to parsing the heterogeneity of psychopathy. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice. 2004;11:69–94.

