Deficits in cross-race face learning: insights from eye movements and pupillometry
- PMID: 19686008
- PMCID: PMC2871406
- DOI: 10.1037/a0016548
Deficits in cross-race face learning: insights from eye movements and pupillometry
Abstract
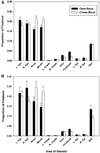
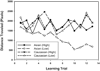
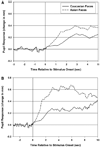
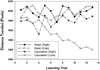
The own-race bias (ORB) is a well-known finding wherein people are better able to recognize and discriminate own-race faces, relative to cross-race faces. In 2 experiments, participants viewed Asian and Caucasian faces, in preparation for recognition memory tests, while their eye movements and pupil diameters were continuously monitored. In Experiment 1 (with Caucasian participants), systematic differences emerged in both measures as a function of depicted race: While encoding cross-race faces, participants made fewer (and longer) fixations, they preferentially attended to different sets of features, and their pupils were more dilated, all relative to own-race faces. Also, in both measures, a pattern emerged wherein some participants reduced their apparent encoding effort to cross-race faces over trials. In Experiment 2 (with Asian participants), the authors observed the same patterns, although the ORB favored the opposite set of faces. Taken together, the results suggest that the ORB appears during initial perceptual encoding. Relative to own-race face encoding, cross-race encoding requires greater effort, which may reduce vigilance in some participants.
(c) 2009 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Althoff RR, Cohen NJ. Eye-movement-based memory effect: A reprocessing effect in face perception. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. 1999;25:997–1010. - PubMed
-
- Anthony T, Copper C, Mullen B. Cross-racial facial identification: A social cognitive integration. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. 1992;18:296–301.
-
- Beatty J. Task-evoked pupillary responses, processing load, and the structure of processing resources. Psychological Bulletin. 1982;91:276–292. - PubMed
-
- Brown G, Kinderman S, Siegle G, Granholm E, Wong E, Burton R. Brain activation and pupil response during covert performance of the Stroop Colour Word task. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 1999;5:308–319. - PubMed

