Use of self-to-object and object-to-object spatial relations in locomotion
- PMID: 19686010
- PMCID: PMC2774707
- DOI: 10.1037/a0016273
Use of self-to-object and object-to-object spatial relations in locomotion
Abstract
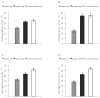
In 8 experiments, the authors examined the use of representations of self-to-object or object-to-object spatial relations during locomotion. Participants learned geometrically regular or irregular layouts of objects while standing at the edge or in the middle and then pointed to objects while blindfolded in 3 conditions: before turning (baseline), after rotating 240 degrees (updating), and after disorientation (disorientation). The internal consistency of pointing in the disorientation condition was equivalent to that in the updating condition when participants learned the regular layout. The internal consistency of pointing was disrupted by disorientation when participants learned the irregular layout. However, when participants who learned the regular layout were instructed to use self-to-object spatial relations, the effect of disorientation on pointing consistency appeared. When participants who learned the irregular layout at the periphery of the layout were instructed to use object-to-object spatial relations, the effect of disorientation disappeared. These results suggest that people represent both self-to-object and object-to-object spatial relations and primarily use object-to-object spatial representation in a regular layout and self-to-object spatial representation in an irregular layout.
(c) 2009 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Burgess N. Spatial memory: how egocentric and allocentric combine. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 2006;10:551–557. - PubMed
-
- Easton RD, Sholl MJ. Object-array structure, frames of reference, and retrieval of spatial knowledge. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. 1995;21:483–500. - PubMed
-
- Holmes MC, Sholl MJ. Allocentric coding of object-to-object relations in overlearned and novel environments. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. 2005;31:1069–1087. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa T, Montello DR. Spatial knowledge acquisition from direct experience in the environment: Individual differences in the development of metric knowledge and the integration of separately learned places. Cognitive Psychology. 2006;52:93–129. - PubMed
-
- Klatzky RL. Allocentric and egocentric spatial representations: Definitions, distinctions, and interconnections. In: Freksa C, Habel C, Wender KF, editors. Spatial cognition: An interdisciplinary approach to representing and processing spatial knowledge LNAI. Vol. 1404. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1998. pp. 1–17.

