Processing umami and other tastes in mammalian taste buds
- PMID: 19686109
- PMCID: PMC3717262
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04107.x
Processing umami and other tastes in mammalian taste buds
Abstract
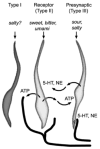
Neuroscientists are now coming to appreciate that a significant degree of information processing occurs in the peripheral sensory organs of taste prior to signals propagating to the brain. Gustatory stimulation causes taste bud cells to secrete neurotransmitters that act on adjacent taste bud cells (paracrine transmitters) as well as on primary sensory afferent fibers (neurocrine transmitters). Paracrine transmission, representing cell-cell communication within the taste bud, has the potential to shape the final signal output that taste buds transmit to the brain. The following paragraphs summarize current thinking about how taste signals generally, and umami taste in particular, are processed in taste buds.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Signal transduction and information processing in mammalian taste buds.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Aug;454(5):759-76. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0247-x. Epub 2007 Apr 28. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17468883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taste buds: cells, signals and synapses.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017 Aug;18(8):485-497. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.68. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28655883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Tripartite Synapses" in Taste Buds: A Role for Type I Glial-like Taste Cells.J Neurosci. 2021 Dec 1;41(48):9860-9871. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1444-21.2021. Epub 2021 Oct 25. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34697094 Free PMC article.
-
Cell communication in taste buds.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 Jul;63(13):1494-500. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6112-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16732426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gustatory signaling in the periphery: detection, transmission, and modulation of taste information.Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(11):1772-7. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1772. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010. PMID: 21048297 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Taste Receptor 2 Subtypes in Human Testis and Sperm.J Clin Med. 2020 Jan 18;9(1):264. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010264. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 31963712 Free PMC article.
-
Bitter Taste Receptors Expression in Human Granulosa and Cumulus Cells: New Perspectives in Female Fertility.Cells. 2021 Nov 11;10(11):3127. doi: 10.3390/cells10113127. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reutter K. Taste organ in the bullhead (Teleostei) Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1978;55:3–94. - PubMed
-
- Roper SD. The cell biology of vertebrate taste receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:329–353. - PubMed
-
- Yee CL, Yang R, Bottger B, et al. “Type III” cells of rat taste buds: immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies of neuron-specific enolase, protein gene product 9.5, and serotonin. J Comp Neurol. 2001;440:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Clapp TR, Yang R, Stoick CL, et al. Morphologic characterization of rat taste receptor cells that express components of the phospholipase C signaling pathway. J Comp Neurol. 2004;468:311–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

