Measuring taste impairment in epidemiologic studies: the Beaver Dam Offspring Study
- PMID: 19686191
- PMCID: PMC2729771
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04103.x
Measuring taste impairment in epidemiologic studies: the Beaver Dam Offspring Study
Abstract
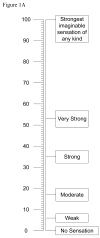
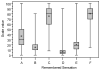
Taste or gustatory function may play an important role in determining diet and nutritional status and therefore indirectly impact health. Yet there have been few attempts to study the spectrum of taste function and dysfunction in human populations. Epidemiologic studies are needed to understand the impact of taste function and dysfunction on public health, to identify modifiable risk factors, and to develop and test strategies to prevent clinically significant dysfunction. However, measuring taste function in epidemiologic studies is challenging and requires repeatable, efficient methods that can measure change over time. Insights gained from translating laboratory-based methods to a population-based study, the Beaver Dam Offspring Study (BOSS) will be shared. In this study, a generalized labeled magnitude scale (gLMS) method was used to measure taste intensity of filter paper disks saturated with salt, sucrose, citric acid, quinine, or 6-n-propylthiouracil, and a gLMS measure of taste preferences was administered. In addition, a portable, inexpensive camera system to capture digital images of fungiform papillae and a masked grading system to measure the density of fungiform papillae were developed. Adult children of participants in the population-based Epidemiology of Hearing Loss Study in Beaver Dam, Wisconsin, are eligible for this ongoing study. The parents were residents of Beaver Dam and 43-84 years of age in 1987-1988; offspring ranged in age from 21-84 years in 2005-2008. Methods will be described in detail and preliminary results about the distributions of taste function in the BOSS cohort will be presented.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Factors related to fungiform papillae density: the beaver dam offspring study.Chem Senses. 2013 Oct;38(8):669-77. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjt033. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Chem Senses. 2013. PMID: 23821729 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on population-based epidemiological studies of olfactory and taste impairment.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Jul;1170:514-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04597.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19686188 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory impairment in adults.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Jul;1170:531-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04102.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19686189 Free PMC article.
-
Intensity of Salt Taste and Prevalence of Hypertension Are Not Related in the Beaver Dam Offspring Study.Chemosens Percept. 2012 Jun 1;5(2):139-145. doi: 10.1007/s12078-012-9118-8. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Chemosens Percept. 2012. PMID: 22745848 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Fungiform Papillae Count on Taste Perception and Different Methods of Taste Assessment and their Clinical Applications: A comprehensive review.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2019 Aug;19(3):e184-e191. doi: 10.18295/squmj.2019.19.03.003. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2019. PMID: 31728215 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New chemosensory component in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES): first-year results for measured olfactory dysfunction.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016 Jun;17(2):221-40. doi: 10.1007/s11154-016-9364-1. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016. PMID: 27287364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population-based epidemiologic studies of aging: the contributions of a Wisconsin community.WMJ. 2009 Aug;108(5):271-2. WMJ. 2009. PMID: 19743764 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Carotid atherosclerosis and cognitive function in midlife: the Beaver Dam Offspring Study.Atherosclerosis. 2011 Nov;219(1):330-3. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.07.013. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Atherosclerosis. 2011. PMID: 21831374 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Bitterness Intensity between Prednisolone and Quinine in a Human Sensory Test Indicated Individual Differences in Bitter-Taste Perception.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 14;14(11):2454. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112454. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36432645 Free PMC article.
-
Taste impairment in chronic rhinosinusitis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018 Jul;8(7):783-789. doi: 10.1002/alr.22113. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018. PMID: 29569385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cruickshanks KJ, Wiley TL, Tweed TS, Klein BEK, Klein R, Mares-Perlman JA, Nondahl DM. Prevalence of hearing loss in older adults in Beaver Dam, WI: The Epidemiology of Hearing Loss Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1998;148(9):879–86. - PubMed
-
- Cruickshanks KJ, Tweed TS, Wiley TL, Klein BEK, Klein R, Chappell RJ, Nondahl DM, Dalton DS. The five-year incidence and progression of hearing loss: The Epidemiology of Hearing Loss Study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;129:1041–1046. - PubMed
-
- Klein R, Klein BE, Linton KL, De Mets DL. The Beaver Dam Eye Study: visual acuity. Ophthalmology. 1991 Aug;98(8):1310–5. - PubMed
-
- Bartoshuk LM, Duffy VB, Green BG, Hoffman HJ, Ko CW, Lucchina LA, Marks LE, Snyder DJ, Weiffenbach JM. Valid across-group comparisons with labeled scales: the gLMS vs magnitude matching. Physiol Behav. 2004;82:109–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

