Psychophysical effects of nasal and oral inflammation
- PMID: 19686197
- PMCID: PMC7168078
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04370.x
Psychophysical effects of nasal and oral inflammation
Abstract
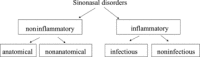
Olfactory disorders are common in "nasal inflammation" even though the term is comprehensive and subsumes different kinds of entities which have to be differentiated. The most common cause of olfactory disorders are sinonasal disorders, which are defined as secondary smell disorders caused by diseases/pathologies in the nose/paranasal sinuses. According to the literature, sinonasal disorders represent--depending on the examined population-up to 72% of all olfactory disorders. In general, noninflammatory and inflammatory disorders are differentiated. Inflammatory disorders can be further classified into infectious or noninfectious disorders, both forms in which olfactory disorders can be present. For the clinician examining patients, the exact classification of the olfactory disorder is mandatory in order to choose appropriate treatment and counseling. Among the most common inflammatory disorders are acute rhinitis, allergic rhinitis, post-upper respiratory tract infection and chronic rhinosinusitis, which are discussed in detail. In contrast to nasal inflammation, only little is known about oral inflammation and its psychophysical effects on taste function. Taste disorders following oral inflammation are briefly discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Damm, M. , Temmel A., Welge‐Luessen A., et al 2004. Epidemiologie und Therapie von Riechstörungen in Deutschland, Österrreich und der Schweiz. HNO 52: 112–120. - PubMed
-
- Mott, A.E. & Leopold D.A.. 1991. Disorders in taste and smell. Med. Clin. North Am. 75: 1321–1353. - PubMed
-
- Nordin, S. , Murphy C., Davidson T.M., et al 1996. Prevalence and assessment of qualitative olfactory dysfunction in different age groups. Laryngoscope 106: 739–742. - PubMed
-
- Deems, D.A. , Doty R.L., Settle G., et al 1991. Smell and taste disorders, a study of 750 patients from the University of Pennsylvania smell and taste center. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 117: 519–528. - PubMed
-
- Akerlund, A. , Bende M. & Murphy C.. 1995. Olfactory threshold and nasal mucosal changes in experimentally induced common cold. Acta Otolaryngol. 115: 88–92. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical