Roles of opioid receptor subtypes in mediating alcohol-seeking induced by discrete cues and context
- PMID: 19686472
- PMCID: PMC2772149
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06851.x
Roles of opioid receptor subtypes in mediating alcohol-seeking induced by discrete cues and context
Abstract
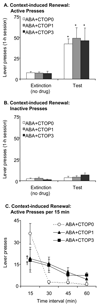
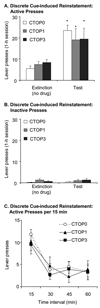
The aim of this study was to assess the effects of selective blockade of the delta (DOP) or mu (MOP) opioid receptors on alcohol-seeking induced by discrete cues and context. In Experiment 1, rats were trained to self-administer alcohol in an environment with distinct sensory properties. After extinction in a different context with separate sensory properties, rats were tested for context-induced renewal in the original context following treatment with the DOP receptor antagonist naltrindole (0-15 mg/kg, i.p.) or the MOP receptor antagonist D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH(2) (CTOP) (0-3 microg/4 microL, i.c.v.). In Experiment 2, reinstatement was tested with the presentation of a discrete light + tone cue previously associated with alcohol delivery, following extinction without the cue. The effects of naltrindole (0-5 mg/kg, i.p.) or CTOP (0-3 microg/4 microL, i.c.v.) were assessed. For context-induced renewal, 7.5 mg/kg naltrindole reduced responding without affecting locomotor activity. Both doses of CTOP attenuated responding in the first 15 min of the renewal test session; however, total responses did not differ at the end of the session. For discrete-cue-induced reinstatement, 1 and 5 mg/kg naltrindole attenuated responding but CTOP had no effect. We conclude that whereas DOP receptors mediate alcohol-seeking induced by discrete cues and context, MOP receptors may play a modest role only in context-induced renewal. These findings point to a differential involvement of opioid receptor subtypes in the effects of different kinds of conditioned stimuli on alcohol-seeking and support a more prominent role for DOP receptors.
Figures


References
-
- Badiani A, Leone P, Stewart J. Intra-VTA injections of the mu-opioid antagonist CTOP enhance locomotor activity. Brain Res. 1995;690:112–116. - PubMed
-
- Burattini C, Gill TM, Aicardi G, Janak PH. The ethanol self-administration context as a reinstatement cue: acute effects of naltrexone. Neuroscience. 2006;139:877–887. - PubMed
-
- Ciccocioppo R, Lin D, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F. Reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior by drug cues following single versus multiple ethanol intoxication in the rat: effects of naltrexone. Psychopharmacology. 2003;168:208–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

