Short- and long-term effects of anti-CD20 treatment on B cell ontogeny in bone marrow of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 19686595
- PMCID: PMC2745807
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2789
Short- and long-term effects of anti-CD20 treatment on B cell ontogeny in bone marrow of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: In the present study we evaluated changes in the B cell phenotype in peripheral blood and bone marrow (BM) of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) following anti-CD20 treatment using rituximab.
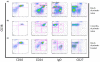
Methods: Blood and BM samples were obtained from 37 patients with RA prior to rituximab treatment. Ten of these patients were resampled 1 month following rituximab, 14 patients after 3 months and the remaining 13 patients were included in the long-term follow up. B cell populations were characterized by CD27/IgD/CD38/CD24 expression.
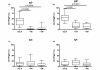
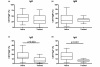
Results: One and three months following rituximab BM retained up to 30% of B cells while circulation was totally depleted of B cells. Analysis of the remaining BM B cells showed prevalence of immature and/or transitional B cells (CD38++CD24++) and CD27+IgD- memory cells, while IgD+ cells were completely depleted. A significant reduction of CD27+ cells in BM and in circulation was observed long after rituximab treatment (mean 22 months), while levels of naive B cells in BM and in circulation were increased. The levels of rheumatoid factor decline after rituximab treatment but returned to baseline levels at the time of retreatment.
Conclusions: Anti-CD20 treatment achieves a depletion of IgD+ B cells shortly after the treatment. At the long term follow up, a reduction of CD27+ B cells was observed in blood and BM. The prolonged inability to up-regulate CD27 may inhibit the renewal of memory B cells. This reduction of CD27+ B cells does not prevent autoantibody production suggesting that mechanisms regulating the formation of auto reactive clones are not disrupted by rituximab.
Figures

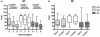

Similar articles
-
Rituximab therapy reduces activated B cells in both the peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: depletion of memory B cells correlates with clinical response.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(4):R131. doi: 10.1186/ar2798. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19715572 Free PMC article.
-
Regeneration of B cell subsets after transient B cell depletion using anti-CD20 antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Aug;54(8):2377-86. doi: 10.1002/art.22019. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16869000
-
Bone marrow B-lineage cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis following rituximab therapy.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007 Jan;46(1):29-36. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kel148. Epub 2006 May 30. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. PMID: 16735454
-
Effects of rituximab therapy on B cell differentiation and depletion.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 May;39(5):1415-1421. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-04996-7. Epub 2020 Feb 22. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32088800 Review.
-
Long-term effects of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: clinical, biologic, and pharmacogenetic aspects.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Sep;1173:692-700. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04668.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19758217 Review.
Cited by
-
B-cell subpopulations in humans and their differential susceptibility to depletion with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S3. doi: 10.1186/ar3908. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 23566754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of rituximab treatment on T and B cell subsets in lymph node biopsies of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Jun 1;58(6):1075-1085. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key428. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30649469 Free PMC article.
-
Standardization of whole blood immune phenotype monitoring for clinical trials: panels and methods from the ONE study.Transplant Res. 2013 Oct 25;2(1):17. doi: 10.1186/2047-1440-2-17. Transplant Res. 2013. PMID: 24160259 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination in Children With Autoimmune Disorders and Treated With Various Immunosuppressive Regimens: A Comprehensive Review and Practical Guide.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 2;12:711637. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.711637. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34408752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human T-follicular helper and T-follicular regulatory cell maintenance is independent of germinal centers.Blood. 2014 Oct 23;124(17):2666-74. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-07-585976. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25224411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takemura S, Klimiuk PA, Braun A, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. T cell activation in rheumatoid synovium is B cell dependent. J Immunol. 2001;167:4710–4718. - PubMed
-
- Wipke BT, Wang Z, Nagengast W, Reichert DE, Allen PM. Staging the initiation of autoantibody-induced arthritis: a critical role for immune complexes. J Immunol. 2004;172:7694–7702. - PubMed
-
- Drossaers-Bakker KW, de Buck M, van Zeben D, Zwinderman AH, Breedveld FC, Hazes JM. Long-term course and outcome of functional capacity in rheumatoid arthritis: the effect of disease activity and radiologic damage over time. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:1854–1860. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199909)42:9<1854::AID-ANR9>3.0.CO;2-F. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

