Outcome of acute prosthetic joint infections due to gram-negative bacilli treated with open debridement and retention of the prosthesis
- PMID: 19687237
- PMCID: PMC2772308
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00188-09
Outcome of acute prosthetic joint infections due to gram-negative bacilli treated with open debridement and retention of the prosthesis
Abstract
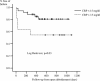
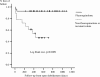
The aim of our study was to evaluate the outcome of acute prosthetic joint infections (PJIs) due to gram-negative bacilli (GNB) treated without implant removal. Patients with an acute PJI due to GNB diagnosed from 2000 to 2007 were prospectively registered. Demographics, comorbidity, type of implant, microbiology data, surgical treatment, antimicrobial therapy, and outcome were recorded. Classification and regression tree analysis, the Kaplan-Meier survival method, and the Cox regression model were applied. Forty-seven patients were included. The mean age was 70.7 years, and there were 15 hip prostheses and 32 knee prostheses. The median number of days from the time of arthroplasty was 20. The most frequent pathogens were members of the Enterobacteriaceae family in 41 cases and Pseudomonas spp. in 20 cases. Among the Enterobacteriaceae, 14 were resistant to ciprofloxacin, while all Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were susceptible to ciprofloxacin. The median durations of intravenous and oral antibiotic treatment were 14 and 64 days, respectively. A total of 35 (74.5%) patients were in remission after a median follow-up of 463 days (interquartile range, 344 to 704) days. By use of the Kaplan-Meier survival curve, a C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration of < or = 15 mg/dl (P = 0.03) and receipt of a fluoroquinolone, when all GNB isolated were susceptible (P = 0.0009), were associated with a better outcome. By use of a Cox regression model, a CRP concentration of < or = 15 mg/dl (odds ratio [OR], 3.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.05 to 12.5; P = 0.043) and receipt of a fluoroquinolone (OR, 9.09; 95% CI, 1.96 to 50; P = 0.005) were independently associated with better outcomes. Open debridement without removal of the implant had a success rate of 74.5%, and the factors associated with good prognosis were a CRP concentration at the time of diagnosis < or = 15 mg/dl and treatment with a fluoroquinolone.
Figures
References
-
- Barberan, J., L. Aguilar, G. Carroquino, M. J. Giménez, B. Sánchez, D. Martínez, and J. Prieto. 2006. Conservative treatment of staphylococcal prosthetic joint infections in elderly patients. Am. J. Med. 119:e7-e10. - PubMed
-
- Giulieri, S. G., P. Graber, P. E. Ochsner, and W. Zimmerli. 2004. Management of infection associated with total hip arthroplasty according to a treatment algorithm. Infection 32:222-228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

