Impact of fish oil-based lipid emulsion on serum triglyceride, bilirubin, and albumin levels in children with parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease
- PMID: 19687773
- PMCID: PMC3377973
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181bbdf2b
Impact of fish oil-based lipid emulsion on serum triglyceride, bilirubin, and albumin levels in children with parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease
Abstract
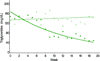
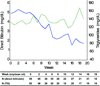
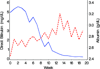
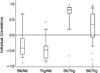
Parenteral nutrition is known to cause liver injury in babies. The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of different lipid emulsions on parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis in infants. In addition, there may be a relationship between the lipid emulsion and triglyceride levels. Furthermore, triglyceride levels may correlate with direct bilirubin and albumin, as markers of liver impairment and nutritional status. Patients with parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis who were treated with a fish oil-based lipid emulsion (n = 18) were prospectively followed for triglyceride, direct bilirubin, and albumin levels and compared with patients who were maintained on a soy-based lipid emulsion (n = 59). Triglyceride levels decreased in the fish oil cohort from a mean of 140 mg/dL at wk 0 to 40 mg/dL at wk 20 but remained unchanged at approximately 140 mg/dL in the soybean cohort. Triglyceride levels of patients treated with fish oil declined over time, while those receiving soybean oil did not. Also, changes in triglyceride levels over time were directly correlated with direct bilirubin and inversely related to albumin levels. These findings may indicate an added benefit of reduced triglyceride levels for patients treated with fish oil and this effect coincides with markers for improved liver function and nutritional status.
Figures



References
-
- Buchman A. Total parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2002;26:S43–S48. - PubMed
-
- Freund HR. Abnormalities of liver function and hepatic damage associated with total parenteral nutrition. Nutrition. 1991;7:1–5. discussion 5–6. - PubMed
-
- Kubota A, Yonekura T, Hoki M, Oyanagi H, Kawahara H, Yagi M, Imura K, Iiboshi Y, Wasa K, Kamata S, Okada A. Total parenteral nutrition-associated intrahepatic cholestasis in infants: 25 years' experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2000;35:1049–1051. - PubMed
-
- Mullick FG, Moran CA, Ishak KG. Total parenteral nutrition: a histopathologic analysis of the liver changes in 20 children. Mod Pathol. 1994;7:190–194. - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Gura KM, Kim S, Arsenault DA, Bistrian BR, Puder M. Current clinical applications of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. Nutr Clin Pract. 2006;21:323–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

