The signaling function of the IL-13Ralpha2 receptor in the development of gastrointestinal fibrosis and cancer surveillance
- PMID: 19689301
- PMCID: PMC11005999
- DOI: 10.2174/156652409788970652
The signaling function of the IL-13Ralpha2 receptor in the development of gastrointestinal fibrosis and cancer surveillance
Abstract
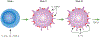
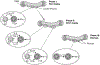
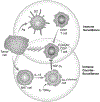
The IL-13Ralpha2 receptor is a high affinity receptor for IL-13 that is used only by IL-13 and is quite distinct from the well known IL-13Ralpha1 receptor that IL-13 shares with IL-4. It was widely considered to be a secreted receptor that is devoid of signaling activity and functional only as a decoy receptor that retarded signaling via IL-13Ralpha1. In recent studies, however, it was shown to be capable of robust signaling that results in production of TGF-beta1 and through the latter cytokine, the induction of fibrosis occuring in various experimental inflammatory states. Thus, in initial studies, IL-13 signaling via IL-13Ralpha2 was shown to play an important role in the fibrosis developing in both oxazolone colitis and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis; later, it was also shown to be critical to the development of fibrosis in a model of chronic colitis induced by trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (TNBS). These studies suggest that blockade of IL-13 or IL-13Ralpha2 signaling might be an excellent target for the prevention of inflammation-associated fibrosis. A second role of IL-13 signaling via IL-13Ralpha2 is in tumor immune surveillance. Thus, in the relevant studies it was shown that NKT cells stimulated by tumor antigens produce IL-13 that then acts on Gr-1 cells to induce TGF-beta1; the latter then inhibits CD8+ T cells engaged in tumor immune surveillance; in effect, then, receptor signaling favors tumor growth. In addition to its signaling function and the induction of TGF-beta1, IL-13Ralpha2 also influences IL-13Ralpha1 signaling in complex ways; thus, IL-13Ralpha2 emerges as a important component of IL-13 signaling, not only in its own right but also in its possible effect on its companion receptor.
Figures
References
-
- Aman MJ, Tayebi N, Obiri NI, Puri RK, Modi WS, Leonard WJ (1996) J. Biol. Chem, 271, 29265–29270. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson DD, Whitters MJ, Fitz LJ, Neben TY, Finnerty H, Henderson SL, O'Hara RM Jr., Beier DR, Turner KJ, Wood CR and Collins M (1998) J. Immunol, 161, 2317–2324. - PubMed
-
- Daines MO, Tabata Y, Walker BA, Chen W, Warrier MR, Basu S and Hershey GK (2006) J. Immunol, 176, 7495–7501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
