Facile self-assembly of neutral dendritic metallocycles via oxygen-to-platinum coordination
- PMID: 19691266
- PMCID: PMC2749078
- DOI: 10.1021/jo9013589
Facile self-assembly of neutral dendritic metallocycles via oxygen-to-platinum coordination
Abstract
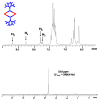
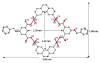
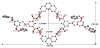
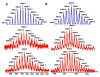
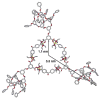
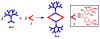
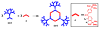
A new approach for the fabrication of neutral dendritic metallocycles is described. By combining rigid 120 degrees dicarboxylate donor linkers funtionalized with [G0]-[G3] Frechet-type dendrons and complementary rigid 60 degrees and 120 degrees di-Pt(II) acceptor subunits, neutral rhomboidal metallodendrimers and hexagonal metallodendrimers, respectively, were prepared under mild conditions in high yields. The assemblies have well-defined shapes and sizes and were characterized by multinuclear NMR ((1)H and (31)P), mass spectrometry (ESI (+)-TOF-MS and APPI(+)-TOF-MS), and elemental analysis. Isotopically resolved mass spectrometry data support the formation of the neutral [2 + 2] rhomboidal, and [3 + 3] hexagonal metallodendrimers, and NMR data are consistent with the formation of all ensembles. The structures of the [G0] and [G1] neutral rhomboidal metallodendrimers (3a and 3b) were unambiguously confirmed via single-crystal X-ray crystallography. The shape and size of [G3] neutral hexagonal metallodendrimer 5d was established with MMFF force-field simulations.
Figures



References
-
- Lehn JM. Supramolecular Chemistry: concepts and perspectives. VCH; New York: 1995.
- Constable EC. Polymer Transition Metal Helicates. Vol. 9. Ibid; 1996. p. 213. Chapter 6.
- Chambron JC, Dietrich-Buchecker C, Sauvage JP. Transition Metals as Assembling and Templating Species. In: Lehn JM, Chair E, Atwood JL, Davis JED, MacNicol DD, Vogtle F, editors. Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry. Vol. 9. Pergamon Press; Oxford: 1996. p. 43. Chapter 2.
- Uller E, Demleitner I, Bernt I, Saalfrank RW. Synergistic Effect of Serendipity and Rational Design in Supramolecular Chemistry. In: Fujita M, editor. Structure and Bonding. Vol. 96. Springer; Berlin: 2000. p. 149.
- Leininger S, Olenyuk B, Stang PJ. Chem Rev. 2000;100:853–908. - PubMed
- Schwab PFH, Levin MD, Michl J. Chem Rev. 1999;99:1863. - PubMed
-
- Stang PJ, Olenyuk B. Acc Chem Res. 1997;30:502.
- Holliday BJ, Mirkin CA. Angew Chem, Int Ed. Vol. 40. 2001. p. 2022. - PubMed
- Seidel SR, Stang PJ. Acc Chem Res. 2002;35:972. - PubMed
- Fujita M, Umemoto K, Yoshizawa M, Fujita N, Kusukawa T, Biradha K. Chem Commun. 2001:509.
- Caulder DL, Raymond KN. Acc Chem Res. 1999;32:975.
- Gianneschi NC, Masar MS, III, Mirkin CA. Acc Chem Res. 2005;38:825. - PubMed
- Cotton FA, Lin C, Murillo CA. Acc Chem Res. 2001;34:759. - PubMed
- Fujita M, Tominaga M, Hori A, Therrien B. Acc Chem Res. 2005;38:369. - PubMed
- Fiedler D, Leung DH, Bergman RG, Raymond KN. Acc Chem Res. 2005;38:349. - PubMed
- Steel PJ. Acc Chem Res. 2005;38:243. - PubMed
- Zangrando E, Casanova M, Alessio E. Chem Rev. 2008;108:4979. - PubMed
- Oliveri CG, Ulmann PA, Wiester MJ, Mirkin CA. Acc Chem Res. 2008;41:1618. - PMC - PubMed
- Lee SJ, Hupp JT. Coord Chem Rev. 2006;250:1710.
-
- Fujita M, Oguro D, Miyazawa M, Oka H, Yamaguchi K, Ogura K. Nature. 1995;378:469.
- Olenyuk B, Levin MD, Whiteford JA, Shield JE, Stang PJ. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:10434.
- Olenyuk B, Whiteford JA, Fechtenkotter A, Stang PJ. Nature. 1999;398:796. - PubMed
- Takeda N, Umemoto K, Yamaguchi K, Fujita M. Nature. 1999;398:794.
- Fujita M, Fujita N, Ogura K, Yamaguchi K. Nature. 1999;400:52.
- Lee SJ, Lin W. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:4554. - PubMed
- Kuehl CJ, Kryschenko YK, Radhakrishnan U, Seidel SR, Huang SD, Stang PJ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:4932. - PMC - PubMed
- Huang XC, Zhang JP, Chen XM. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:13218. - PubMed
- Davis AV, Raymond KN. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:7912. - PubMed
- Hiraoka S, Sakata Y, Shionoya M. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:10058. - PubMed
- Hiraoka S, Harano K, Shiro M, Ozawa Y, Yasuda N, Toriumi K, Shionoya M. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2006;45:6488. - PubMed
- Merlau ML, Del Pilar Mejia M, Nguyen ST, Hupp JT. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2001;40:4239. - PubMed
- Sun SS, Stern CL, Nguyen ST, Hupp JT. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:6314. - PubMed
- Murase T, Sato S, Fujita M. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2007;46:1083. - PubMed
- Kawano M, Kawamichi T, Haneda T, Kojima T, Fujita M. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:15418. - PubMed
- Ghosh S, Mukherjee PS. J Org Chem. 2006;71:8412. - PubMed
-
- Cotton FA, Daniels LM, Lin C, Murillo CA. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:4538.
- Cotton FA, Donahue JP, Murillo CA. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:5436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

