Mean platelet volume as a predictor of cardiovascular risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 19691485
- PMCID: PMC3755496
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03584.x
Mean platelet volume as a predictor of cardiovascular risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether an association exists between mean platelet volume (MPV) and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and other cardiovascular events. Platelet activity is a major culprit in atherothrombotic events. MPV, which is widely available in clinical practice, is a potentially useful biomarker of platelet activity in the setting of cardiovascular disease.
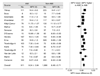
Methods and results: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis investigating the association between MPV and AMI, all-cause mortality following myocardial infarction, and restenosis following coronary angioplasty. Results were pooled using random-effects modeling. Pooled results from 16 cross-sectional studies involving 2809 patients investigating the association of MPV and AMI indicated that MPV was significantly higher in those with AMI than those without AMI [mean difference 0.92 fL, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.67-1.16, P < 0.001). In subgroup analyses, significant differences in MPV existed between subjects with AMI, subjects with stable coronary disease (P < 0.001), and stable controls (P < 0.001), but not vs. those with unstable angina (P = 0.24). Pooled results from three cohort studies involving 3184 patients evaluating the risk of death following AMI demonstrated that an elevated MPV increased the odds of death as compared with a normal MPV (11.5% vs. 7.1%, odds ratio 1.65, 95% CI 1.12-2.52, P = 0.012). Pooled results from five cohort studies involving 430 patients who underwent coronary angioplasty revealed that MPV was significantly higher in patients who developed restenosis than in those who did not develop restenosis (mean difference 0.98 fL, 95% CI 0.74-1.21, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Elevated MPV is associated with AMI, mortality following myocardial infarction, and restenosis following coronary angioplasty. These data suggest that MPV is a potentially useful prognostic biomarker in patients with cardiovascular disease. Whether the relationship is causal, and whether MPV should influence practice or guide therapy, remains unknown.
Conflict of interest statement
D.L. Bhatt discloses the following relationships: Research Grants - Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Ethicon, Heartscape, Sanofi Aventis, The Medicines Company; Consultant/Advisory Board - Arena, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cardax, Centocor, Cogentus, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Glaxo Smith Kline, Johnson & Johnson, McNeil, Medtronic, Millennium, Molecular Insights, Otsuka, Paringenix, PDL, Philips, Portola, Sanofi Aventis, Schering Plough, Scios, Takeda, The Medicines Company, Vertex. The other authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Comment in
-
Mean platelet volume: a quick, easy determinant of thrombotic risk?J Thromb Haemost. 2010 Jan;8(1):146-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03673.x. Epub 2009 Oct 30. J Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 19874471 No abstract available.
References
-
- Davi G, Patrono C. Platelet activation and atherothrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2482–2494. - PubMed
-
- Coppinger JA, Cagney G, Toomey S, Kislinger T, Belton O, McRedmond JP, Cahill DJ, Emili A, Fitzgerald DJ, Maguire PB. Characterization of the proteins released from activated platelets leads to localization of novel platelet proteins in human atherosclerotic lesions. Blood. 2004;103:2096–2104. - PubMed
-
- Meadows TA, Bhatt DL. Clinical aspects of platelet inhibitors and thrombus formation. Circ Res. 2007;100:1261–1275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

