The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis mediates inter-individual variations in anxiety and fear
- PMID: 19692610
- PMCID: PMC2741739
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2119-09.2009
The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis mediates inter-individual variations in anxiety and fear
Abstract
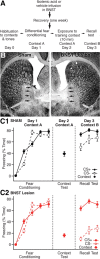
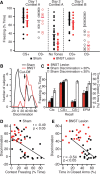
While learning to fear stimuli that predict danger promotes survival, the inability to inhibit fear to inappropriate cues leads to a pernicious cycle of avoidance behaviors. Previous studies have revealed large inter-individual variations in fear responding with clinically anxious humans exhibiting a tendency to generalize learned fear to safe stimuli or situations. To shed light on the origin of these inter-individual variations, we subjected rats to a differential auditory fear conditioning paradigm in which one conditioned auditory stimulus (CS+) was paired to footshocks whereas a second (CS-) was not. We compared the behavior of rats that received pretraining excitotoxic lesions of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) to that of sham rats. Sham rats exhibit a continuum of anxious/fearful behaviors. At one end of the continuum were rats that displayed a poor ability to discriminate between the CS+ and CS-, high contextual freezing, and an anxiety-like trait in the elevated plus maze (EPM). At the other end were rats that display less fear generalization to the CS-, lower freezing to context, and a nonanxious trait in the EPM. Although BNST-lesioned rats acquired similarly high levels of conditioned fear to the CS+, they froze less than sham rats to the CS-. In fact, BNST-lesioned rats behaved like sham rats with high discriminative abilities in that they exhibited low contextual fear and a nonanxious phenotype in the EPM. Overall, this suggests that inter-individual variations in fear generalization and anxiety phenotype are determined by BNST influences on the amygdala and/or its targets.
Figures
Comment in
-
The role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in learning to fear.J Neurosci. 2009 Dec 9;29(49):15351-2. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5194-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 20007458 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Brush FR, Gendron CM, Isaacson MD. A selective genetic analysis of the Syracuse high- and low-avoidance (SHA/Bru and SLA/Bru) strains of rats (Rattus norvegicus) Behav Brain Res. 1999;106:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Burgos-Robles A, Vidal-Gonzalez I, Santini E, Quirk GJ. Consolidation of fear extinction requires NMDA receptor-dependent bursting in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Neuron. 2007;53:871–880. - PubMed
-
- Cohen H, Zohar J, Gidron Y, Matar MA, Belkind D, Loewenthal U, Kozlovsky N, Kaplan Z. Blunted HPA axis response to stress influences susceptibility to posttraumatic stress response in rats. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:1208–1218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
