Gamma-secretase inhibition reduces spine density in vivo via an amyloid precursor protein-dependent pathway
- PMID: 19692615
- PMCID: PMC6665795
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2288-09.2009
Gamma-secretase inhibition reduces spine density in vivo via an amyloid precursor protein-dependent pathway
Abstract
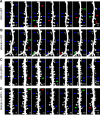
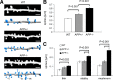
Alzheimer's disease (AD) represents the most common age-related neurodegenerative disorder. It is characterized by the invariant accumulation of the beta-amyloid peptide (Abeta), which mediates synapse loss and cognitive impairment in AD. Current therapeutic approaches concentrate on reducing Abeta levels and amyloid plaque load via modifying or inhibiting the generation of Abeta. Based on in vivo two-photon imaging, we present evidence that side effects on the level of dendritic spines may counteract the beneficial potential of these approaches. Two potent gamma-secretase inhibitors (GSIs), DAPT (N-[N-(3,5-difluorophenacetyl-L-alanyl)]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester) and LY450139 (hydroxylvaleryl monobenzocaprolactam), were found to reduce the density of dendritic spines in wild-type mice. In mice deficient for the amyloid precursor protein (APP), both GSIs had no effect on dendritic spine density, demonstrating that gamma-secretase inhibition decreases dendritic spine density via APP. Independent of the effects of gamma-secretase inhibition, we observed a twofold higher density of dendritic spines in the cerebral cortex of adult APP-deficient mice. This observation further supports the notion that APP is involved in the modulation of dendritic spine density--shown here for the first time in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Comery TA, Martone RL, Aschmies S, Atchison KP, Diamantidis G, Gong X, Zhou H, Kreft AF, Pangalos MN, Sonnenberg-Reines J, Jacobsen JS, Marquis KL. Acute gamma-secretase inhibition improves contextual fear conditioning in the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 2005;25:8898–8902. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dovey HF, John V, Anderson JP, Chen LZ, de Saint Andrieu P, Fang LY, Freedman SB, Folmer B, Goldbach E, Holsztynska EJ, Hu KL, Johnson-Wood KL, Kennedy SL, Kholodenko D, Knops JE, Latimer LH, Lee M, Liao Z, Lieberburg IM, Motter RN, et al. Functional gamma-secretase inhibitors reduce beta-amyloid peptide levels in brain. J Neurochem. 2001;76:173–181. - PubMed
-
- Feng G, Mellor RH, Bernstein M, Keller-Peck C, Nguyen QT, Wallace M, Nerbonne JM, Lichtman JW, Sanes JR. Imaging neuronal subsets in transgenic mice expressing multiple spectral variants of GFP. Neuron. 2000;28:41–51. - PubMed
-
- Fleisher AS, Raman R, Siemers ER, Becerra L, Clark CM, Dean RA, Farlow MR, Galvin JE, Peskind ER, Quinn JF, Sherzai A, Sowell BB, Aisen PS, Thal LJ. Phase 2 safety trial targeting amyloid beta production with a gamma-secretase inhibitor in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2008;65:1031–1038. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
