Clinical practice. Infection associated with prosthetic joints
- PMID: 19692690
- PMCID: PMC2850113
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMcp0905029
Clinical practice. Infection associated with prosthetic joints
Abstract
A 62-year-old woman with osteoarthritis presents with a 7-month history of progressively worsening left hip pain radiating to the groin, 8 months after undergoing total left-hip arthroplasty. The pain has not responded to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Physical examination reveals a sinus tract overlying her left hip. Her leukocyte count is 8000 per cubic millimeter, and the C-reactive protein (CRP) level is 15.5 mg per liter. A radiograph shows loosening of the prosthesis at the bone–cement interface. Synovial-fluid aspirate shows 15×103 cells per cubic millimeter (89% neutrophils); cultures of an aspirate from the hip grow Staphylococcus epidermidis. How should her case be managed?
Figures

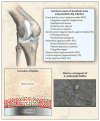

References
-
- National Hospital Discharge Survey: survey results and products. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2009. [Accessed July 24, 2009]. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhds/nhds_products.htm.
-
- Kurtz SM, Lau E, Schmier J, Ong KL, Zhao K, Parvizi J. Infection burden for hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23:984–91. - PubMed
-
- Jämsen E, Huhtala H, Puolakka T, Moilanen T. Risk factors for infection after knee arthroplasty: a register-based analysis of 43,149 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Peersman G, Laskin R, Davis J, Peterson M. Infection in total knee replacement: a retrospective review of 6489 total knee replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;392:15–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
