Heart-rate recovery index is impaired in Behçet's disease
- PMID: 19693299
- PMCID: PMC2720298
Heart-rate recovery index is impaired in Behçet's disease
Abstract
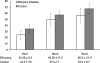
Behçet's disease, a multisystemic inflammatory disorder, has been associated with a number of cardiovascular dysfunctions, including ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Heart-rate recovery after exercise can provide both an estimate of impaired parasympathetic tone and a prognosis in regard to all-cause and cardiovascular death. The aim of our study was to evaluate heart-rate recovery in Behçet's disease. From January through July 2008, we examined at our outpatient clinic and prospectively enrolled 30 consecutive patients with Behçet's disease and 50 healthy control participants who were matched for age and sex. Basal electrocardiography, echocardiography, and treadmill exercise testing were performed in all patients and control participants. The heart-rate recovery index was calculated in the usual manner, by subtracting the 1st-minute (Rec1), 2nd-minute (Rec2), and 3rd-minute (Rec3) recovery heart rates from the maximal heart rate after exercise stress testing. Patients with Behçet's disease exhibited significantly lower heart-rate recovery numbers, compared with healthy control participants: Rec1, 24.28 +/- 8.2 vs 34.4 +/- 7.6, P = 0.002; Rec2, 49.28 +/- 11.2 vs 57.5 +/- 7.0, P < 0.05; and Rec3, 56.2 +/- 12.11 vs 67.4 +/- 8.7, P = 0.014. To our knowledge, this is the 1st study that shows an impaired heart-rate recovery index (indicative of reduced parasympathetic activity) among patients with Behçet's disease. Given the independent prognostic value of the heart-rate recovery index, our results may explain the increased occurrence of arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in Behçet's patients. Therefore, this index may be clinically useful in the identification of high-risk patients.
Keywords: Arrhythmias, cardiac; Behcet syndrome/complications; autonomic nervous system; electrocardiography; exercise test; exercise tolerance; heart rate; nervous system diseases; parasympathetic nervous system; predictive value of tests; prognosis; prospective studies; sympathetic nervous system; tachycardia, ventricular; vagus nerve.
Figures
References
-
- Behcet H. Ueber rezidivierende aphtose, durch ein virus verursachte geschwure am mund, am auge und an den genitalien. Dermatol Wochenschr 1937;105:1152–7.
-
- Akar H, Konuralp C, Akpolat T. Cardiovascular involvement in Behcet's disease. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg 2003;3(3):261–5. - PubMed
-
- Candan I, Erol C, Sonel A, Akalin H. Behcet's disease: cardiac and pulmonary involvement. Eur Heart J 1986;7(11):999–1002. - PubMed
-
- Koc Y, Gullu I, Akpek G, Akpolat T, Kansu E, Kiraz S, et al. Vascular involvement in Behcet's disease. J Rheumatol 1992; 19(3):402–10. - PubMed
-
- Schiff S, Moffatt R, Mandel WJ, Rubin SA. Acute myocardial infarction and recurrent ventricular arrhythmias in Behcet's syndrome. Am Heart J 1982;103(3):438–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
