A framework for brain registration via simultaneous surface and volume flow
- PMID: 19694295
- PMCID: PMC4512671
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-02498-6_48
A framework for brain registration via simultaneous surface and volume flow
Abstract
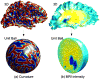
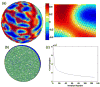
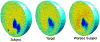
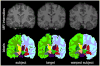
Volumetric registration of brain MR images presents a challenging problem due to the wide variety of sulcal folding patterns. We present a novel volumetric registration method based on an intermediate parameter space in which the shape differences are normalized. First, we generate a 3D harmonic map of each brain volume to unit ball which is used as an intermediate space. Cortical surface features and volumetric intensity are then used to find a simultaneous surface and volume registration. We present a finite element method for the registration by using a tetrahedral volumetric mesh for registering the interior volumetric information and the corresponding triangulated mesh at the surface points. This framework aligns the convoluted sulcal folding patterns as well as the subcortical structures by allowing simultaneous flow of surface and volumes for registration. We describe the methodology and FEM implementation and then evaluate the method in terms of the overlap between segmented structures in coregistered brains.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Geometry driven volumetric registration.Inf Process Med Imaging. 2007;20:675-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-73273-0_56. Inf Process Med Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17633739
-
Brain image registration using cortically constrained harmonic mappings.Inf Process Med Imaging. 2007;20:359-71. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-73273-0_30. Inf Process Med Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17633713 Free PMC article.
-
A combined surface and volumetric registration (SAVOR) framework to study cortical biomarkers and volumetric imaging data.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2009;12(Pt 1):713-20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-04268-3_88. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2009. PMID: 20426051
-
Surface-constrained volumetric brain registration using harmonic mappings.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2007 Dec;26(12):1657-69. doi: 10.1109/tmi.2007.901432. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2007. PMID: 18092736 Free PMC article.
-
Learning best features for deformable registration of MR brains.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2005;8(Pt 2):179-87. doi: 10.1007/11566489_23. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2005. PMID: 16685958
Cited by
-
Deformable medical image registration: a survey.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2013 Jul;32(7):1153-90. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2013.2265603. Epub 2013 May 31. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23739795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole brain diffeomorphic metric mapping via integration of sulcal and gyral curves, cortical surfaces, and images.Neuroimage. 2011 May 1;56(1):162-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.01.067. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 21281722 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Identification of Partial-Correlation Based Networks with Applications to Cortical Thickness Data.Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2012 May;2012:1551-1554. doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2012.6235869. Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2012. PMID: 26753056 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate nonlinear mapping between MNI volumetric and FreeSurfer surface coordinate systems.Hum Brain Mapp. 2018 Sep;39(9):3793-3808. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24213. Epub 2018 May 16. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018. PMID: 29770530 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of micron resolution mouse brain surface from large-scale imaging dataset using resampling-based variational model.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 6;5:12782. doi: 10.1038/srep12782. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26245266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Changeux JP. Drug use and abuse. In: Edelman GM, Changeux J, editors. The Brain. Transaction Publishers; 2001.
-
- Nahas GG, Burks TF, editors. Drug Abuse in the Decade of the Brain. IOS Press; 1997.
-
- Joshi AA, Shattuck DW, Thompson PM, Leahy RM. A finite element method for elastic parameterization and alignment of cortical surfaces using sulcal constraints. Proc of ISBI. 2007
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
