Immune-mediated mechanisms potentially regulate the disease time-course of duchenne muscular dystrophy and provide targets for therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 19695529
- PMCID: PMC2779711
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2009.04.010
Immune-mediated mechanisms potentially regulate the disease time-course of duchenne muscular dystrophy and provide targets for therapeutic intervention
Abstract
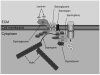
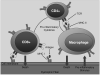
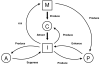
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a lethal muscle-wasting disease that affects boys. Mutations in the dystrophin gene result in the absence of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex (DGC) from muscle plasma membranes. In healthy muscle fibers, the DGC forms a link between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton to protect against contraction-induced membrane lesions and to regulate cell signaling. The absence of the DGC results in aberrant regulation of inflammatory signaling cascades. Inflammation is a key pathological characteristic of dystrophic muscle lesion formation. However, the role and regulation of this process in the disease time-course has not been sufficiently examined. The transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB has been shown to contribute to the disease process and is likely involved with increased inflammatory gene expression, including cytokines and chemokines, found in dystrophic muscle. These aberrant signaling processes may regulate the early time-course of inflammatory events that contribute to the onset of disease. This review critically evaluates the possibility that dystrophic muscle lesions in both patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and mdx mice are the result of immune-mediated mechanisms that are regulated by inflammatory signaling and also highlights new therapeutic directions.
Figures


References
-
- Blake DJ, Weir A, Newey SE, Davies KE. Function and genetics of dystrophin and dystrophin-related proteins in muscle. Physiol. Rev. 2002;82:291–329. - PubMed
-
- Tidball JG, Wehling-Henricks M. Evolving therapeutic strategies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: targeting downstream events. Pediatr. Res. 2004;56:831–841. - PubMed
-
- Straub V, Campbell KP. Muscular dystrophies and the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 1997;10:168–175. - PubMed
-
- Durbeej M, Campbell KP. Muscular dystrophies involving the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex: an overview of current mouse models. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002;12:349–361. - PubMed
-
- Oak SA, Zhou YW, Jarrett HW. Skeletal muscle signaling pathway through the dystrophin glycoprotein complex and Rac1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:39287–39295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

