FoxM1, a critical regulator of oxidative stress during oncogenesis
- PMID: 19696738
- PMCID: PMC2760115
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.239
FoxM1, a critical regulator of oxidative stress during oncogenesis
Abstract
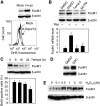
The transcription factor FoxM1 is over-expressed in most human malignancies. Although it is evident that FoxM1 has critical functions in tumour development and progression, the mechanisms by which FoxM1 participates in those processes are not understood. Here, we describe an essential role of FoxM1 in the regulation of oxidative stress that contributes to malignant transformation and tumour cell survival. We identify a negative feedback loop involving FoxM1 that regulates reactive oxygen species (ROS) in proliferating cells. We show that induction of FoxM1 by oncogenic Ras requires ROS. Elevated FoxM1, in turn, downregulates ROS levels by stimulating expression of ROS scavenger genes, such as MnSOD, catalase and PRDX3. FoxM1 depletion sensitizes cells to oxidative stress and increases oncogene-induced premature senescence. Moreover, tumour cells expressing activated AKT1 are 'addicted' to FoxM1, as they require continuous presence of FoxM1 for survival. Together, our results identify FoxM1 as a key regulator of ROS in dividing cells, and provide insights into the mechanism how tumour cells use FoxM1 to control oxidative stress to escape premature senescence and apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Bass DA, Parce JW, Dechatelet LR, Szejda P, Seeds MC, Thomas M (1983) Flow cytometric studies of oxidative product formation by neutrophils: a graded response to membrane stimulation. J Immunol 130: 1910–1917 - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868 - PubMed
-
- Burdon RH (1995) Superoxide and hydrogen peroxide in relation to mammalian cell proliferation. Free Radic Biol Med 18: 775–794 - PubMed
-
- Burgering BM, Medema RH (2003) Decisions on life and death: FOXO Forkhead transcription factors are in command when PKB/Akt is off duty. J Leukoc Biol 73: 689–701 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA 124488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA090764/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA124488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG025953/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK 44525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG021842/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA090764/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG016927/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK044525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG024138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK068503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021842/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG024138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100035/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 100035/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025953/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016927/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

