Altered white matter microstructure in adolescent substance users
- PMID: 19699064
- PMCID: PMC2734872
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2009.04.005
Altered white matter microstructure in adolescent substance users
Abstract
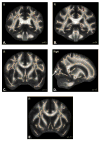
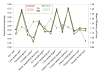
Chronic marijuana use during adolescence is frequently comorbid with heavy alcohol consumption and associated with CNS alterations, yet the influence of early cannabis and alcohol use on microstructural white matter integrity is unclear. Building on evidence that cannabinoid receptors are present in myelin precursors and affect glial cell processing, and that excessive ethanol exposure is associated with persistently impaired myelination, we used diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to characterize white matter integrity in heavy substance using and non-using adolescents. We evaluated 36 marijuana and alcohol-using (MJ+ALC) adolescents (ages 16-19) and 36 demographically similar non-using controls with DTI. The diffusion parameters fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) were subjected to whole-brain voxelwise group comparisons using tract-based spatial statistics (Smith, S.M., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T.E., Mackay, C.E., Watkins, K.E., Ciccarelli, O., Cader, M.Z., Matthews, P.M., Behrens, T.E., 2006. Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31, 1487-1505). MJ+ALC teens had significantly lower FA than controls in 10 regions, including left superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF), left postcentral gyrus, bilateral crus cerebri, and inferior frontal and temporal white matter tracts. These diminutions occurred in the context of increased FA in right occipital, internal capsule, and SLF regions. Changes in MD were less distributed, but increased MD was evident in the right occipital lobe, whereas the left inferior longitudinal fasciculus showed lower MD in MJ+ALC users. Findings suggest that fronto-parietal circuitry may be particularly impacted in adolescent users of the most prevalent intoxicants: marijuana and alcohol. Disruptions to white matter in this young group could indicate aberrant axonal and myelin maturation with resultant compromise of fiber integrity. Findings of increased anisotropic diffusion in alternate brain regions suggest possible neuroadaptive processes and can be examined in future studies of connectivity to determine how aberrancies in specific tracts might influence efficient cognitive processing.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach T, Rescorla L. Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, and Families; 2001.
-
- Andersson JL, Skare S. A model-based method for retrospective correction of geometric distortions in diffusion-weighted EPI. Neuroimage. 2002;16:177–199. - PubMed
-
- Arnone D, Barrick TR, Chengappa S, Mackay CE, Clark CA, Abou-Saleh MT. Corpus callosum damage in heavy marijuana use: preliminary evidence from diffusion tensor tractography and tract-based spatial statistics. Neuroimage. 2008;41:1067–1074. - PubMed
-
- Ashtari M, Cervellione KL, Hasan KM, Wu J, McIlree C, Kester H, Ardekani BA, Roofeh D, Szeszko PR, Kumra S. White matter development during late adolescence in healthy males: a cross-sectional diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuroimage. 2007;35:501–510. - PubMed

