Deubiquitinase activities required for hepatocyte growth factor-induced scattering of epithelial cells
- PMID: 19699092
- PMCID: PMC2764384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.040
Deubiquitinase activities required for hepatocyte growth factor-induced scattering of epithelial cells
Abstract
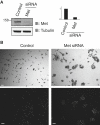
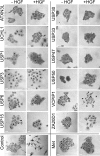
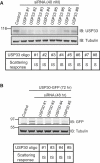
The scattering response of epithelial cells to activation of the Met receptor tyrosine kinase represents one facet of an "invasive growth" program. It is a complex event that incorporates loss of cell-cell adhesion, morphological changes, and cell motility. Ubiquitination is a reversible posttranslational modification that may target proteins for degradation or coordinate signal transduction pathways. There are approximately 79 active deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) predicted in the human genome. Here, via a small interfering RNA (siRNA) library approach, we have identified 12 DUBs that are necessary for aspects of the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-dependent scattering response of A549 cells. Different phenotypes are evident that range from full loss of scattering, similar to receptor knockdown (e.g., USP30, USP33, USP47), to loss of cell-cell contacts even in the absence of HGF but defective motility (e.g., USP3, ATXN3L). The knockdowns do not incur defective receptor, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, or MAP kinase activation. Our data suggest widespread involvement of the ubiquitin system at multiple stages of the Met activation response, implying significant crosstalk with phosphorylation-based transduction pathways. Development of small-molecule inhibitors of particular DUBs may offer a therapeutic approach to contain metastasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cooperative effect of hepatocyte growth factor and fibronectin in anchorage-independent survival of mammary carcinoma cells: requirement for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity.Cell Growth Differ. 2000 Feb;11(2):123-33. Cell Growth Differ. 2000. PMID: 10714768
-
Mechanisms of hepatocyte growth factor-induced retinal endothelial cell migration and growth.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000 Jun;41(7):1885-93. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000. PMID: 10845613
-
The SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein 1 (SSB-1) interacts with MET and enhances the hepatocyte growth factor-induced Erk-Elk-1-serum response element pathway.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 22;280(16):16393-401. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413897200. Epub 2005 Feb 15. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15713673
-
Inhibition of junction assembly in cultured epithelial cells by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor is concomitant with increased stability and altered phosphorylation of the soluble junctional molecules.Cell Growth Differ. 1997 Apr;8(4):451-62. Cell Growth Differ. 1997. PMID: 9101091
-
Structure, biosynthesis and biochemical properties of the HGF receptor in normal and malignant cells.EXS. 1993;65:131-65. EXS. 1993. PMID: 8380735 Review.
Cited by
-
A targeted in vivo RNAi screen reveals deubiquitinases as new regulators of Notch signaling.G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Dec;2(12):1563-75. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.003780. Epub 2012 Dec 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 23275879 Free PMC article.
-
USP50 suppresses alternative RecQ helicase use and deleterious DNA2 activity during replication.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 16;15(1):8102. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52250-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39284827 Free PMC article.
-
USP30 deubiquitylates mitochondrial Parkin substrates and restricts apoptotic cell death.EMBO Rep. 2015 May;16(5):618-27. doi: 10.15252/embr.201439820. Epub 2015 Mar 4. EMBO Rep. 2015. PMID: 25739811 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ubiquitin-specific protease 9X (USP9X) as a deubiquitinase acting on ubiquitin-peroxin 5 (PEX5) thioester conjugate.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 13;287(16):12815-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.340158. Epub 2012 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22371489 Free PMC article.
-
Supervillin-mediated suppression of p53 protein enhances cell survival.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 15;288(11):7918-7929. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.416842. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23382381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birchmeier C., Birchmeier W., Gherardi E., Vande Woude G.F. Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:915–925. - PubMed
-
- Gentile A., Trusolino L., Comoglio P.M. The Met tyrosine kinase receptor in development and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27:85–94. - PubMed
-
- Hunter T. The age of crosstalk: Phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and beyond. Mol. Cell. 2007;28:730–738. - PubMed
-
- Welchman R.L., Gordon C., Mayer R.J. Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins as multifunctional signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005;6:599–609. - PubMed
-
- Scheel, H. (2005). Comparative analysis of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in Homo sapiens and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PhD thesis, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

