Examining polyglutamine peptide length: a connection between collapsed conformations and increased aggregation
- PMID: 19699209
- PMCID: PMC2764006
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.08.034
Examining polyglutamine peptide length: a connection between collapsed conformations and increased aggregation
Abstract
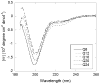
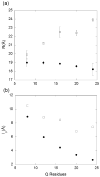
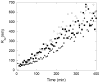
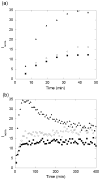
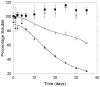
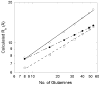
Abnormally expanded polyglutamine domains in proteins are associated with several neurodegenerative diseases, of which the best known is Huntington's. Expansion of the polyglutamine domain facilitates aggregation of the affected protein, and several studies directly link aggregation to neurotoxicity. The age of onset of disease is inversely correlated with the length of the polyglutamine domain; this correlation motivates an examination of the role of the length of the domain on aggregation. In this investigation, peptides containing 8 to 24 glutamines were synthesized, and their conformational and aggregation properties were examined. All peptides lacked secondary structure. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer studies revealed that the peptides became increasingly collapsed as the number of glutamine residues increased. The effective persistence length was estimated to decrease from approximately 11 to approximately 7 A as the number of glutamines increased from 8 to 24. A comparison of our data with theoretical results suggests that phosphate-buffered saline is a good solvent for Q8 and Q12, a theta solvent for Q16, and a poor solvent for Q20 and Q24. By dynamic light scattering, we observed that Q16, Q20, and Q24, but not Q8 or Q12, immediately formed soluble aggregates upon dilution into phosphate-buffered saline at 37 degrees C. Thus, Q16 stands at the transition point between good and poor solvent and between stable and aggregation-prone peptide. Examination of aggregates by transmission electron microscopy, along with kinetic assays for sedimentation, provided evidence indicating that soluble aggregates mature into sedimentable aggregates. Together, the data support a mechanism of aggregation in which monomer collapse is accompanied by formation of soluble oligomers; these soluble species lack regular secondary structure but appear morphologically similar to the sedimentable aggregates into which they eventually mature.
Figures


References
-
- Bates G. Huntingtin aggregation and toxicity in Huntington’s disease. Lancet. 2003;361:1642–1644. - PubMed
-
- Orr HT. Beyond the Qs in the polyglutamine diseases. Genes Dev. 2001;15:925–932. - PubMed
-
- Wanker EE. Protein aggregation and pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease: mechanisms and correlations. Biol Chem. 2000;381:937–942. - PubMed
-
- Gusella JF, MacDonald ME. Molecular genetics: unmasking polyglutamine triggers in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000;1:109–115. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht M, Golatta M, Wullner U, Lengauer T. Structural and functional analysis of ataxin-2 and ataxin-3. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:3155–3170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

