Non-coding RNA transcripts: sensors of neuronal stress, modulators of synaptic plasticity, and agents of change in the onset of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19699259
- PMCID: PMC2767472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.08.032
Non-coding RNA transcripts: sensors of neuronal stress, modulators of synaptic plasticity, and agents of change in the onset of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
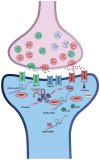
Non-protein-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) play critical roles on many levels of cellular information processing and pervasive expression of ncRNAs in the nervous system could help explain brain complexity. NcRNAs are enriched in the central nervous system and are associated with specific neuroanatomical regions. Additionally, several recent publications have revealed an important role for deregulation of ncRNAs in various human neuropathologies, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and Fragile X mental retardation. Herein, we summarize reports on functional ncRNA molecules involved in cellular stress response, particularly related to Alzheimer's disease. We conclude that ncRNAs have a prominent role in maintaining precise physiological levels of gene products directly implicated in Alzheimer's disease pathology.
Figures
References
-
- St Laurent G, 3rd, Wahlestedt C. Noncoding RNAs: couplers of analog and digital information in nervous system function? Trends Neurosci. 2007;30:612–21. - PubMed
-
- Gagen MJ, Mattick JS. Accelerating, hyperaccelerating, and decelerating networks. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2005;72:016123. - PubMed
-
- Taft RJ, Pheasant M, Mattick JS. The relationship between non-protein-coding DNA and eukaryotic complexity. Bioessays. 2007;29:288–99. - PubMed
-
- Mattick JS. A new paradigm for developmental biology. J Exp Biol. 2007;210:1526–47. - PubMed
-
- Mattick JS. RNA regulation: a new genetics? Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:316–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

