A novel fibronectin type III module binding motif identified on C-terminus of Leptospira immunoglobulin-like protein, LigB
- PMID: 19699715
- PMCID: PMC2804977
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.089
A novel fibronectin type III module binding motif identified on C-terminus of Leptospira immunoglobulin-like protein, LigB
Abstract
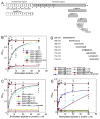
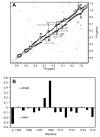
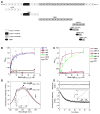
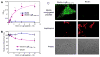
Infection by pathogenic strains of Leptospira hinges on the pathogen's ability to adhere to host cells via extracellular matrix such as fibronectin (Fn). Previously, the immunoglobulin-like domains of Leptospira Lig proteins were recognized as adhesins binding to N-terminal domain (NTD) and gelatin binding domain (GBD) of Fn. In this study, we identified another Fn-binding motif on the C-terminus of the Leptospira adhesin LigB (LigBCtv), residues 1708-1712 containing sequence LIPAD with a beta-strand and nascent helical structure. This motif binds to 15th type III modules (15F(3)) (K(D)=10.70 microM), and association (k(on)=600 M(-1)s(-1)) and dissociation (k(off)=0.0129 s(-1)) rate constants represents a slow binding kinetics in this interaction. Moreover, pretreatment of MDCK cells with LigB(1706-1716) blocked the binding of Leptospira by 39%, demonstrating a significant role of LigB(1706-1716) in cellular adhesion. These data indicate that the LIPAD residues (LigB(1708-1712)) of the Leptospira interrogans LigB protein bind 15F(3) of Fn at a novel binding site, and this interaction contributes to adhesion to host cells.
Figures
References
-
- Faine SB, Adher B, Bolin C, et al. Leptospira and Leptospirosis. MedSci; Melbourne, Australia: 1999.
-
- Schwarz-Linek U, Hook M, Potts JR. The molecular basis of fibronectin-mediated bacterial adherence to host cells. Mol Microbiol. 2004;52:631–641. - PubMed
-
- Lin YP, Chang YF. A domain of the Leptospira LigB contributes to high affinity binding of fibronectin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;362:443–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

