Orexin/hypocretin modulation of the basal forebrain cholinergic system: Role in attention
- PMID: 19699722
- PMCID: PMC2819645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.08.046
Orexin/hypocretin modulation of the basal forebrain cholinergic system: Role in attention
Abstract
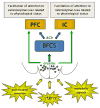
The basal forebrain cholinergic system (BFCS) plays a role in several aspects of attentional function. Activation of this system by different afferent inputs is likely to influence how attentional resources are allocated. While it has been recognized for some time that the hypothalamus is a significant source of projections to the basal forebrain, the phenotype(s) of these inputs and the conditions under which their regulation of the BFCS becomes functionally relevant are still unclear. The cell bodies of neurons expressing orexin/hypocretin neuropeptides are restricted to the lateral hypothalamus and contiguous perifornical area but have widespread projections, including to the basal forebrain. Orexin fibers and both orexin receptor subtypes are distributed in cholinergic parts of the basal forebrain, where application of orexin peptides increases cell activity and cortical acetylcholine release. Furthermore, disruption of orexin signaling in the basal forebrain impairs the cholinergic response to an appetitive stimulus. In this review, we propose that orexin inputs to the BFCS form an anatomical substrate for links between arousal and attention, and that these interactions might be particularly important as a means by which interoceptive cues bias allocation of attentional resources toward related exteroceptive stimuli. Dysfunction in orexin-acetylcholine interactions may play a role in the arousal and attentional deficits that accompany neurodegenerative conditions as diverse as drug addiction and age-related cognitive decline.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Akiyama M, Yuasa T, Hayasaka N, Horikawa K, Sakurai T, Shibata S. Reduced food anticipatory activity in genetically orexin (hypocretin) neuron-ablated mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20:3054–62. - PubMed
-
- Ammoun S, Holmqvist T, Shariatmadari R, Oonk HB, Detheux M, Parmentier M, Akerman KE, Kukkonen JP. Distinct recognition of OX1 and OX2 receptors by orexin peptides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;305:507–14. - PubMed
-
- Arnold H, Burk J, Hodgson E, Sarter M, Bruno J. Differential cortical acetylcholine release in rats performing a sustained attention task versus behavioral control tasks that do not explicitly tax attention. Neuroscience. 2002;114:451. - PubMed
-
- Arnold HM, Nelson CL, Sarter M, Bruno JP. Sensitization of cortical acetylcholine release by repeated administration of nicotine in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2003;165:346–58. - PubMed
-
- Backberg M, Hervieu G, Wilson S, Meister B. Orexin receptor-1 (OX-R1) immunoreactivity in chemically identified neurons of the hypothalamus: focus on orexin targets involved in control of food and water intake. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;15:315–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

