A novel GABAergic afferent input to the pontine reticular formation: the mesopontine GABAergic column
- PMID: 19699725
- PMCID: PMC2766548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.08.045
A novel GABAergic afferent input to the pontine reticular formation: the mesopontine GABAergic column
Abstract
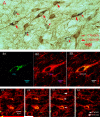
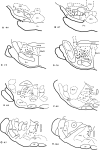
Pharmacological manipulations of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmission in the nucleus pontis oralis (PnO) of the rat brainstem produce alterations in sleep/wake behavior. Local applications of GABA(A) receptor antagonists and agonists increase REM sleep and wake, respectively. These findings support a role for GABAergic mechanisms of the PnO in the control of arousal state. We have been investigating sources of GABA innervation of the PnO that may interact with local GABA(A) receptors in the control of state. Utilizing a retrograde tracer, cholera toxin-B subunit (CTb), injected into the PnO and dual-label immunohistochemistry with an antibody against glutamic acid decarboxalase-67 (GAD67), we report on a previously unidentified GABAergic neuronal population projecting to the contralateral PnO appearing as a column of cells, with long-axis in the sagittal plane, extending through the midbrain and pons. We refer to these neurons as the mesopontine GABAergic column (MPGC). The contiguous, columnar, anatomical distribution suggests operation as a functional neural system, which may influence expression of REM sleep, wake and other behaviors subserved by the PnO.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sleep duration varies as a function of glutamate and GABA in rat pontine reticular formation.J Neurochem. 2011 Aug;118(4):571-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07350.x. Epub 2011 Jul 1. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21679185 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic and non-GABAergic thalamic, hypothalamic and basal forebrain projections to the ventral oral pontine reticular nucleus: their implication in REM sleep modulation.Brain Res. 2008 May 19;1210:116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.095. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18407254
-
Muscarinic-2 and orexin-2 receptors on GABAergic and other neurons in the rat mesopontine tegmentum and their potential role in sleep-wake state control.J Comp Neurol. 2008 Oct 20;510(6):607-30. doi: 10.1002/cne.21803. J Comp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18709662
-
Pontine reticular formation (PnO) administration of hypocretin-1 increases PnO GABA levels and wakefulness.Sleep. 2008 Apr;31(4):453-64. doi: 10.1093/sleep/31.4.453. Sleep. 2008. PMID: 18457232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Modulation by the GABA of the ventro-oral-pontine reticular REM sleep-inducing neurons].An R Acad Nac Med (Madr). 2007;124(2):397-411; discussion 411-3. An R Acad Nac Med (Madr). 2007. PMID: 18069603 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
GABA(A) receptors implicated in REM sleep control express a benzodiazepine binding site.Brain Res. 2013 Aug 21;1527:131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.06.037. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23835499 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic transmission in rat pontine reticular formation regulates the induction phase of anesthesia and modulates hyperalgesia caused by sleep deprivation.Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Jul;40(1):2264-73. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12571. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24674578 Free PMC article.
-
Benzodiazepine receptor agonists cause drug-specific and state-specific alterations in EEG power and acetylcholine release in rat pontine reticular formation.Sleep. 2010 Jul;33(7):909-18. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.7.909. Sleep. 2010. PMID: 20614851 Free PMC article.
-
Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in rat pontine reticular formation increase wakefulness.Sleep. 2013 Mar 1;36(3):337-43. doi: 10.5665/sleep.2444. Sleep. 2013. PMID: 23450652 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep duration varies as a function of glutamate and GABA in rat pontine reticular formation.J Neurochem. 2011 Aug;118(4):571-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07350.x. Epub 2011 Jul 1. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21679185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahnaou A, Basille M, Gonzalez B, Vaudry H, Hamon M, Adrien J, Bourgin P. Long-term enhancement of REM sleep by the pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) in the pontine reticular formation of the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999;11:4051–4058. - PubMed
-
- Ahnaou A, Laporte AM, Ballet S, Escourrou P, Hamon M, Adrien J, Bourgin P. Muscarinic and PACAP receptor interactions at pontine level in the rat: significance for REM sleep regulation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000;12:4496–4504. - PubMed
-
- Baghdoyan HA, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, McCarley RW, Hobson JA. A neuroanatomical gradient in the pontine tegmentum for the cholinoceptive induction of desynchronized sleep signs. Brain Research. 1987;414:245–261. - PubMed
-
- Bier MJ, McCarley RW. REM-enhancing effects of the adrenergic antagonist idazoxan infused to the medial pontine reticular formation of the freely moving cat. Brain Research. 1994;634:333–338. - PubMed
-
- Boissard R, Fort P, Gervasoni D, Barbagli B, Luppi P-H. Localization of the GABAergic and non-GABAergic neurons projecting to the sublaterodorsal nucleus and potentially gating paradoxical sleep onset. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003;18:1627–1639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

