Soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in human heart failure: relation with myocardial function and clinical outcomes
- PMID: 19700132
- PMCID: PMC3179261
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2009.01.014
Soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in human heart failure: relation with myocardial function and clinical outcomes
Abstract
Background: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is an endogenous counterregulator of the renin-angiotensin system. The relationship between soluble ACE2 (sACE2), myocardial function, and clinical outcomes in patients with chronic systolic heart failure is not well established.
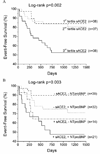
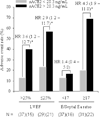
Methods and results: We measured sACE2 activity in 113 patients with chronic systolic heart failure (left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF] <or=35%, New York Heart Association Class II-IV). Comprehensive echocardiography was performed at the time of blood sampling. We prospectively examined adverse clinical events (death, cardiac transplant, and heart failure hospitalizations) over 34 +/- 17 months. Patients who had higher sACE2 plasma activity were more likely to have a lower LVEF (Spearman's r = -0.36, P < .001), greater right ventricular systolic dysfunction (r = 0.33, P < .001), higher estimated pulmonary artery systolic pressure (r = 0.35, P = .002), larger left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (r = 0.23, P = .02), and higher plasma NT-proBNP levels (r = 0.35, P < .001). sACE2 was less associated with diastolic dysfunction (r = 0.19, P = .05), and was similar between patients with ischemic and nonischemic cardiomyopathies. There was no relationship between sACE2 activity and markers of systemic inflammation. After adjusting for NT-proBNP and LVEF, sACE2 activity remained an independent predictor of adverse clinical events (HR = 1.7 [95% CI: 1.1-2.6], P = .018).
Conclusions: Elevated plasma sACE2 activity was associated with greater severity of myocardial dysfunction and was an independent predictor of adverse clinical events.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increasing serum soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activity after intensive medical therapy is associated with better prognosis in acute decompensated heart failure.J Card Fail. 2013 Sep;19(9):605-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2013.06.296. J Card Fail. 2013. PMID: 24054336 Free PMC article.
-
New perspectives in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) IV: circulating ACE2 as a biomarker of systolic dysfunction in human hypertension and heart failure.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 1;9(4):e87845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087845. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24691269 Free PMC article.
-
Role of circulating angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in left ventricular remodeling following myocardial infarction: a prospective controlled study.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 22;8(4):e61695. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061695. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23630610 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in heart failure: insights into the endogenous counter-regulatory pathway of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Aug 26;52(9):750-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.02.088. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18718423 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Soluble angiotensin converting enzyme 2 levels in chronic heart failure is associated with decreased exercise capacity and increased oxidative stress-mediated endothelial dysfunction.Transl Res. 2019 Oct;212:80-88. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2019.06.004. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31323221 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Virus-Receptor Interactions of Glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Human ACE2 Receptor.Cell Host Microbe. 2020 Oct 7;28(4):586-601.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.08.004. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Cell Host Microbe. 2020. PMID: 32841605 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-Receptor Interactions of Glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Human ACE2 Receptor.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 24:2020.06.25.172403. doi: 10.1101/2020.06.25.172403. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell Host Microbe. 2020 Oct 7;28(4):586-601.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.08.004. PMID: 32743578 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Counter-regulatory renin-angiotensin system in cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020 Feb;17(2):116-129. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0244-8. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31427727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACE2 is augmented in dystrophic skeletal muscle and plays a role in decreasing associated fibrosis.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 2;9(4):e93449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093449. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24695436 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced susceptibility to biomechanical stress in ACE2 null mice is prevented by loss of the p47(phox) NADPH oxidase subunit.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Jul 1;91(1):151-61. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr036. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21285291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parmley WW. Evolution of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in hypertension, heart failure, and vascular protection. Am J Med. 1998;105:27S–31S. - PubMed
-
- Packer M, Poole-Wilson PA, Armstrong PW, Cleland JG, Horowitz JD, Massie BM, Ryden L, Thygesen K, Uretsky BF. Comparative effects of low and high doses of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, lisinopril, on morbidity and mortality in chronic heart failure. ATLAS Study Group. Circulation. 1999;100:2312–2318. - PubMed
-
- Der Sarkissian S, Huentelman MJ, Stewart J, Katovich MJ, Raizada MK. ACE2: A novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2006;91:163–198. - PubMed
-
- Mehta PK, Griendling KK. Angiotensin II cell signaling: physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C82–C97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

