Investigation of stoichiometry of T4 bacteriophage helicase loader protein (gp59)
- PMID: 19700405
- PMCID: PMC2785558
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.029926
Investigation of stoichiometry of T4 bacteriophage helicase loader protein (gp59)
Abstract
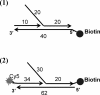
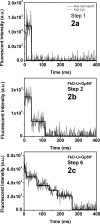
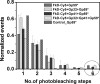
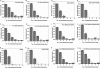
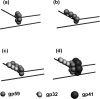
The T4 bacteriophage helicase loader (gp59) is one of the main eight proteins that play an active role in the replisome. gp59 is a small protein (26 kDa) that exists as a monomer in solution and in the crystal. It binds preferentially to forked DNA and interacts directly with the T4 helicase (gp41), single-stranded DNA-binding protein (gp32), and polymerase (gp43). However, the stoichiometry and structure of the functional form are not very well understood. There is experimental evidence for a hexameric structure for the helicase (gp41) and the primase (gp61), inferring that the gp59 structure might also be hexameric. Various experimental approaches, including gel shift, fluorescence anisotropy, light scattering, and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, have not provided a clearer understanding of the stoichiometry. In this study, we employed single-molecule photobleaching (smPB) experiments to elucidate the stoichiometry of gp59 on a forked DNA and to investigate its interaction with other proteins forming the primosome complex. smPB studies were performed with Alexa 555-labeled gp59 proteins and a forked DNA substrate. Co-localization experiments were performed using Cy5-labeled forked DNA and Alexa 555-labeled gp59 in the presence and absence of gp32 and gp41 proteins. A systematic study of smPB experiments and subsequent data analysis using a simple model indicated that gp59 on the forked DNA forms a hexamer. In addition, the presence of gp32 and gp41 proteins increases the stability of the gp59 complex, emphasizing their functional role in T4 DNA replication machinery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction between the T4 helicase loading protein (gp59) and the DNA polymerase (gp43): unlocking of the gp59-gp43-DNA complex to initiate assembly of a fully functional replisome.Biochemistry. 2005 May 31;44(21):7747-56. doi: 10.1021/bi047296w. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15909989
-
Helicase assembly protein Gp59 of bacteriophage T4: fluorescence anisotropy and sedimentation studies of complexes formed with derivatives of Gp32, the phage ssDNA binding protein.Biochemistry. 2001 Jun 26;40(25):7651-61. doi: 10.1021/bi010116n. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11412119
-
Control of helicase loading in the coupled DNA replication and recombination systems of bacteriophage T4.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 31;289(5):3040-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.505842. Epub 2013 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24338568 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of bacteriophage T4 DNA replication: a review in the Virology Journal series on bacteriophage T4 and its relatives.Virol J. 2010 Dec 3;7:359. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-359. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 21129204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PriA and phage T4 gp59: factors that promote DNA replication on forked DNA substrates microreview.Mol Microbiol. 2000 May;36(3):519-27. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01888.x. Mol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10844643 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel method to accurately locate and count large numbers of steps by photobleaching.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Nov 7;27(22):3601-3615. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-06-0404. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27654946 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding DNA replication by the bacteriophage T4 replisome.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 10;292(45):18434-18442. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R117.811208. Epub 2017 Sep 25. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28972188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assembly and dynamics of Gp59-Gp32-single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), a DNA helicase loading complex required for recombination-dependent replication in bacteriophage T4.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 1;287(23):19070-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.343830. Epub 2012 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22500043 Free PMC article.
-
Single molecule photobleaching (SMPB) technology for counting of RNA, DNA, protein and other molecules in nanoparticles and biological complexes by TIRF instrumentation.Methods. 2014 May 15;67(2):169-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Methods. 2014. PMID: 24440482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutational analysis of the T4 gp59 helicase loader reveals its sites for interaction with helicase, single-stranded binding protein, and DNA.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 25;287(22):18596-607. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.332080. Epub 2012 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22427673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benkovic S. J., Valentine A. M., Salinas F. (2001) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70, 181–208 - PubMed
-
- Xi J., Zhang Z., Zhuang Z., Yang J., Spiering M. M., Hammes G. G., Benkovic S. J. (2005) Biochemistry 44, 7747–7756 - PubMed
-
- Nelson S. W., Yang J., Benkovic S. J. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281, 8697–8706 - PubMed
-
- Kreuzer K. N., Yap W. Y., Menkens A. E., Engman H. W. (1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263, 11366–11373 - PubMed
-
- Kreuzer K. N. (2000) Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 165–173 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

